El segundo cerebro: la conexión entre la microbiota intestinal y la salud mental
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.36790/epistemus.v19i38.421Palabras clave:
Microbiota intestinal, Salud mental, Intestino-cerebro, Neurotransmisores, ProbióticosResumen
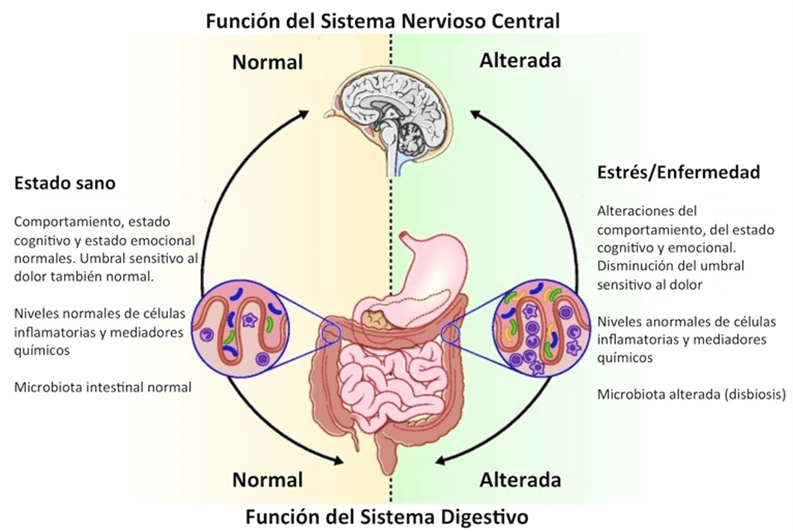
La microbiota intestinal ha emergido como un componente clave en la regulación de la salud mental humana, mediando procesos a través del eje microbiota-intestino-cerebro. Este artículo tiene como objetivo analizar la relación entre el intestino y el cerebro, destacando los mecanismos mediante los cuales la microbiota intestinal influye en el estado de ánimo, el comportamiento y diversos trastornos neuropsiquiátricos. Para ello, se revisa el papel del sistema nervioso entérico, la producción de neurotransmisores, y el impacto de factores como la dieta, el estrés y el uso de probióticos. Los hallazgos sugieren que mantener un equilibrio adecuado en la microbiota intestinal no solo favorece la salud digestiva, sino que puede ser un factor determinante en la prevención y el tratamiento complementario de trastornos mentales, consolidando la idea del intestino como un “segundo cerebro” con influencia directa en nuestro bienestar emocional.
Descargas
Citas
M. D. Gershon, The Second Brain: A Groundbreaking New Understanding of Nervous Disorders of the Stomach and Intestine, HarperCollins, Noviembre 1999.
R. Campo-Moreno, T. Alarcón-Cavero, G. D’Auria, S. Delgado-Palacio, y M. Ferrer-Martínez, “Microbiota en la salud humana: técnicas de caracterización y transferencia,” Elsevier España, vol. 36, núm. 4, pp. 241-245, Abril 2018. DOI: 10.1016/j.eimc.2017.02.007
J. Sebastián-Domingo, y C. Sánchez-Sánchez, “De la flora intestinal al microbioma. Revista Española de Enfermedades Digestivas,” Revista Española de Enfermedades Digestivas, vol. 110, núm. 1, pp. 51-56, Diciembre 2018. DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.17235/reed.2017.4947/2017
R. Garza, S. Garza y L. Perea, “Microbiota intestinal: aliada fundamental del organismo humano,” Educación química, vol. 32, no. 1, pp. 10-19, Agosto 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.22201/fq.18708404e.2021.1.75734
M. E. Icaza-Chávez, “Microbiota intestinal en la salud y la enfermedad,” Revista de Gastroenterología de México, vol. 78, núm. 4, pp. 240-248, Diciembre 2013. DOI: 10.1016/j.rgmx.2013.04.004
J. Cryan, K. O’riordan, C. Cowan, K. Sandhu, T. Bastiaanssen, M. Boehme, M. Codagnone, S. Cussotto, C. Fulling, A. Golubeva, K. Guzzetta, M. Jaggar, C. Long-Smith, J. Lyte, J. Martin, A. Molinero-Perez, G. Moloney, E. Morelli, E. Morillas, R. O’Connor, J. Cruz-Pereira, V. Peterson, K. Rea, N. Ritz, E. Sherwin, S. Spichak, E. Teichman, M. van de Wouw, P. Ventura-Silva, S. Wallace-Fitzsimons, N. Hyland, G. Clarke y T. Dinan, “The microbiota-gut-brain axis,” Physiological Reviews, vol. 99, no. 4, pp. 1877-2013, Octubre 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00018.2018
M. Saraf, B. Piccolo, A. Bowlin, K. Mercer, T. LeRoith, S. Chintapalli, K. Shankar, T. Badger y L. Yeruva, “Formula diet driven microbiota shifts tryptophan metabolism from serotonin to tryptamine in neonatal porcine colon,” Microbiome, vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 1-13, Julio 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40168-017-0297-z
K. Yoshii, K. Hosomi, K. Sawane y J. Kunisawa, “Metabolism of dietary and microbial vitamin b family in the regulation of host immunity,” Frontiers in Nutrition, vol. 6, pp. 1-13, Abril 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2019.00048
B. Ramakrishna, “Role of the gut microbiota in human nutrition and metabolism," Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, vol. 28, pp. 9-17, Diciembre 2013. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.12294
C. Cortés, A. Escobar, J. Cebada, G. Soto, T. Bilbao y M. Vélez, “Estrés y cortisol: implicaciones en la ingesta de alimento,” Revista Cubana de Investigaciones Biomédicas, vol. 37, no. 3, pp. 1-15, 2018. ISSN: 1561-3011
M. Gómez-Eguílaz, J. L. Ramón-Trapero, L. Pérez-Martínez y J. R. Blanco, “El eje microbiota-intestino-cerebro y sus grandes proyecciones,” Rev. Neurol, vol. 68, núm. 3, pp. 111-117, Febrero 2019. PMID: 30687918
M. Peñafiel, y K. Novo, “Eje intestino-cerebro y su impacto en el estrés,” RECIAMUC, vol. 7, núm. 2, pp. 576-584, Junio 2023. DOI: https://doi.org/10.26820/reciamuc/7.(2).abril.2023.576-584
J. Álvarez, J. Real, F. Guarner, M. Gueimonde, J. Rodríguez, M. De Pipaón, y Y. Sanz, “Microbiota intestinal y salud,” Gastroenterología y Hepatología, vol. 44, núm. 7, pp. 519-535, Septiembre 2021. DOI: 10.1016/j.gastrohep.2021.01.009
H. Kaur, C. Bose y S. Mande, “Tryptophan Metabolism by Gut Microbiome and Gut-Brain-Axis: An in silico Analysis,” Frontiers in Neuroscience, vol. 13, núm. 1365, Diciembre 2019. DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2019.01365
Z. Barandouzi, J. Lee, M. del Carmen, J. Chen, W. Henderson, A. Starkweather y X. Cong, “Associations of neurotransmitters and the gut microbiome with emotional distress in mixed type of irritable bowel syndrome,” Sci Rep, vol. 12, pp 1-8, Enero 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-05756-0
Y. Orbe-Orihuela, J. Hernández-Mariano, A. Castañeda-Márquez, y A. Alvarado-Delgado, “Microbiota intestinal y su relación con la salud mental,” XIKUA Boletín Científico de la Escuela Superior de Tlahuelilpan, vol. 12, núm. 23, pp. 69-75, Enero 2024. DOI: https://doi.org/10.29057/xikua.v12i23.11673
P. Strandwitz, “Neurotransmitter modulation by the gut microbiota,” Brain Research, vol. 1693, pp. 128-133, Agosto 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2018.03.015
G. Álvarez, F. Guarner, T. Requena, y M. Ascensión, “Dieta y microbiota. Impacto en la salud,” Nutrición Hospitalaria, vol. 35, núm. 6, pp. 11-15, Julio 2020. DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.20960/nh.2280
F. Jiménez-Trejo, “Coevolución microbiota-humano y sus implicaciones en salud: de cazadores-recolectores a sedentarios industrializados,” Revista del Centro de Investigación de la Universidad La Salle, vol. 14, núm. 56, pp. 1-16, Diciembre 2021. DOI: http://doi.org/10.26457/recein.v14i56.2859
R. Kelly, Y. Borre, C. O' Brien, E. Patterson, S. El Aidy, J. Deane, P. J. Kennedy, S. Beers, K. Scott, G. Moloney, A. E. Hoban, L. Scott, P. Fitzgerald, P. Ross, C. Stanton, G. Clarke, J. F. Cryan, y T. G. Dinan, “Transferring the blues: Depression-associated gut microbiota induces neurobehavioural changes in the rat,” Journal of Psychiatric Research, vol. 82, pp. 109-118, Noviembre 2019. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2016.07.019
L. Fuenmayor-González, T. Fajardo-Loaiza, J. Rivadeneira-Dueñas, y J. Arévalo-Mancheno, “Microbiota, probióticos y el comportamiento humano,” Revista Vive, vol. 5, núm. 13, pp. 75-86, Febrero 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.33996/revistavive.v5i13.1132
C. Scorza, C. Piccini y P. Zunino. "Microbiota intestinal, probióticos y salud mental," Revista de Psiquiatría del Uruguay, vol. 83, núm. 1, pp. 33-42, Octubre 2019. Recuperado de: http://spu.org.uy/sitio/wp-content/uploads/2019/10/04_REV_02.pdf
C. Wallace, y R. Milev, “Los efectos de los probióticos sobre los síntomas depresivos en humanos: una revisión sistemática,” Ann Gen Psychiatry, vol. 16, núm. 14, Febrero 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12991-017-0138-2
D. Silva, B. Vicente y M. Valdivia, “Factor neurotrófico derivado del cerebro como marcador de conducta suicida en pacientes con trastorno depresivo mayor,” Revista chilena de neuro-psiquiatría, vol.53, no. 1, pp. 44-52, Marzo 2015. DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4067/S0717-92272015000100006
A. Gómez-López, “Microbioma, salud y enfermedad: probióticos, prebióticos y simbióticos,” Biomédica, vol. 39, núm. 4, pp. 617-621, Diciembre 2019. PMID: 31860173
J. Gao, L. Zhao, Y. Cheng, W. Lei, Y. Wang, X. Liu, N. Zheng, L. Shao, X. Chen, Y. Sun, Z. Ling, y W. Xu, “ Probiotics for the treatment of depression and its comorbidities: A systemic review,” Frontiers in cellular and infection microbiology, vol. 13, pp. 2-4, Abril 2023. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2023.1167116
C. Castañeda, “Microbiota intestinal y trastornos del comportamiento mental,” Revista Cubana de Pediatría, vol. 92, núm. 2, Abril 2020. ISSN: 1561-3119
K. Hashimoto, “Emerging role of the host microbiome in neuropsychiatric disorders: overview and future directions,” Mol Psychiatry, vol. 28, pp. 3625-3627, Octubre 2023. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-023-02287-6
C. Lin, H. Yang y H. Lane, “D-glutamate, D-serine, and D-alanine differ in their roles in cognitive decline in patients with Alzheimer’s disease or mild cognitive impairment,” Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior, vol. 185, pp. 1-6, Octubre 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2019.172760
V. Nikolova, M. Smith, L. Hall, J. Cleare, J. M. Stone y A. Young, “Perturbations in gut microbiota composition in psychiatric disorders: a review and meta-analysis,” JAMA Psych, vol. 78, pp. 1343-1354, Septiembre 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2021.2573
S. Kumari, R. Taliyan y S. Dubey, “Comprehensive review on potential signaling pathways involving the transfer of α-synuclein from the gut to the brain that leads to Parkinson’s disease,” ACS Chem Neurosci, vol. 14, pp. 590-602, Febrero 2023. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acschemneuro.2c00730
Descargas
Publicado
Cómo citar
Número
Sección
Licencia
Derechos de autor 2025 EPISTEMUS

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-CompartirIgual 4.0.
La revista adquiere los derechos patrimoniales de los artículos sólo para difusión sin ningún fin de lucro, sin menoscabo de los propios derechos de autoría.
Los autores son los legítimos titulares de los derechos de propiedad intelectual de sus respectivos artículos, y en tal calidad, al enviar sus textos expresan su deseo de colaborar con la Revista Epistemus, editada semestralmente por la Universidad de Sonora.
Por lo anterior, de manera libre, voluntaria y a título gratuito, una vez aceptado el artículo para su publicación, ceden sus derechos a la Universidad de Sonora para que la Universidad de Sonora edite, publique, distribuya y ponga a disposición a través de intranets, internet o CD dicha obra, sin limitación alguna de forma o tiempo, siempre y cuando sea sin fines de lucro y con la obligación expresa de respetar y mencionar el crédito que corresponde a los autores en cualquier utilización que se haga del mismo.
Queda entendido que esta autorización no es una cesión o transmisión de alguno de sus derechos patrimoniales en favor de la mencionada institución. La UniSon le garantiza el derecho de reproducir la contribución por cualquier medio en el cual usted sea el autor, sujeto a que se otorgue el crédito correspondiente a la publicación original de la contribución en Epistemus.
Salvo indicación contraria, todos los contenidos de la edición electrónica se distribuyen bajo una licencia de uso y Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0) Puede consultar desde aquí la versión informativa y el texto legal de la licencia. Esta circunstancia ha de hacerse constar expresamente de esta forma cuando sea necesario.