Detección de metales en agua a través de teléfonos inteligentes
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.36790/epistemus.v17i35.299Palabras clave:
colorimetría, metales pesados, teléfonos inteligentesResumen
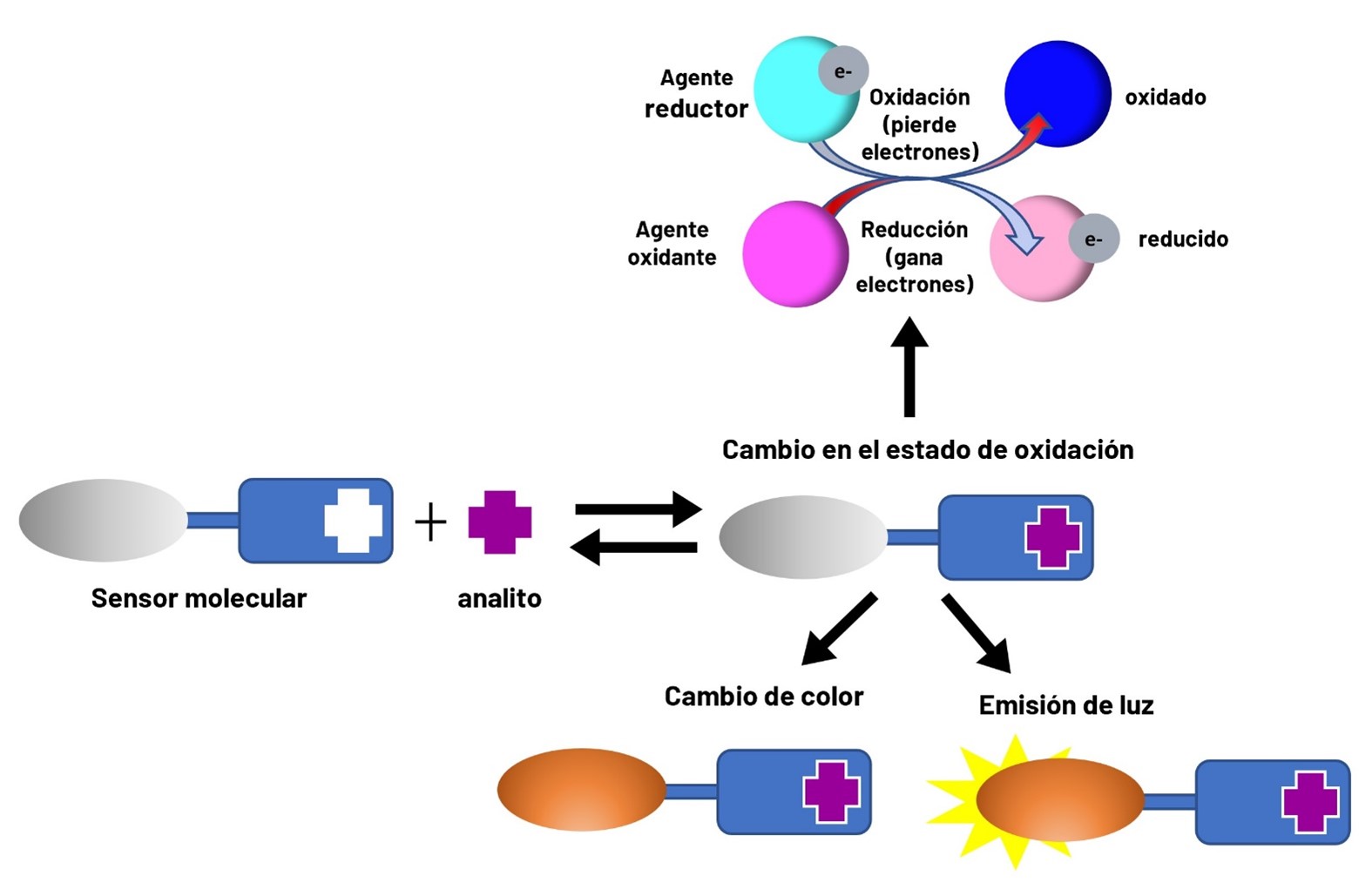
El interés por instrumentos analíticos portables que permitan la detección de metales al alcance de más usuarios ha crecido en los últimos años. Los teléfonos inteligentes se han convertido en laboratorios portátiles. La Química Analítica encontró en los teléfonos una oportunidad para detectar y cuantificar diferentes analitos en tiempo y espacio real sin la necesidad de realizar análisis en el laboratorio (un ejemplo es la detección colorimétrica de metales en agua). En este artículo de divulgación se expone el alcance de los teléfonos inteligentes como herramientas para la detección de metales. Además, se plantea un caso de estudio en el que se utilizó una película sensora biodegradable a base de almidón, gelatina y un indicador colorimétrico para la detección de cobre, zinc y níquel.
Descargas
Citas
INEGI, “Encuesta Nacional sobre Disponibilidad y Uso de Tecnologías de la Información en los Hogares”, 2020. Recuperado de: https://www.inegi.org.mx/contenidos/saladeprensa/boletines/2021/OtrTemEcon/ENDUTIH_2020.pdf
Sivakumar, Rajamanickam, and Nae Yoon Lee. “Recent Progress in Smartphone-Based Techniques for Food Safety and the Detection of Heavy Metal Ions in Environmental Water” in Chemosphere, 2021, 275 (July): 130096. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHEMOSPHERE.2021.130096. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130096
Y. Zhang, T. Xue, L. Cheng, J. Wang, R. Shen, J. Zhang, Smartphone-assisted colorimetric biosensor for on-site detection of Cr3+ ion analysis, Anal. Chim. Acta. 1199 (2022) 339603. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ACA.2022.339603. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2022.339603
M.L. Firdaus, A. Aprian, N. Meileza, M. Hitsmi, R. Elvia, L. Rahmidar, R. Khaydarov, Smartphone Coupled with a Paper-Based Colorimetric Device for Sensitive and Portable Mercury Ion Sensing, (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors7020025. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors7020025
N. Emmanuel, R. Haridas, S. Chelakkara, R.B. Nair, A. Gopi, M. Sajitha, K. Yoosaf, Smartphone Assisted Colourimetric Detection and Quantification of Pb2+and Hg2+Ions Using Ag Nanoparticles from Aqueous Medium, IEEE Sens. J. 20 (2020) 8512–8519. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2020.2984580. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2020.2984580
An-Liang Zhang (2021) Smartphone-Based Colorimetric Detection of Heavy Metal Copper (II) Ion by Help of Surface Acoustic Wave, Ferroelectrics, 583:1, 41-50, https://doi.org/10.1080/00150193.2021.1980326 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/00150193.2021.1980326
Njue, N., Stenfert Kroese, J., Gräf, J., Jacobs, S. R., Weeser, B., Breuer, L., & Rufino, M. C. (2019). Citizen science in hydrological monitoring and ecosystem services management: State of the art and future prospects. Science of the Total Environment, 693, 133531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.07.337 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.07.337
Priyadarshanee, Monika, and Surajit Das. “Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering Biosorption and Removal of Toxic Heavy Metals by Metal Tolerating Bacteria for Bioremediation of Metal Contamination : A Comprehensive Review” in Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104686. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104686
Alloway, B. J.; Ayres, D. C., Chemical principles of environmental pollution. Blackie Academic and Professional. An imprint of Chapman and Hall. Oxford, UK: 1993. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-2148-4
Ayangbenro, Ayansina Segun, and Olubukola Oluranti Babalola. “A New Strategy for Heavy Metal Polluted Environments: A Review of Microbial Biosorbents” in International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2017, 14 (1): 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14010094. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14010094
Hong, Y. J., Liao, W., Yan, Z. F., Bai, Y. C., Feng, C. L., Xu, Z. X., & Xu, D. Y. (2020). Progress in the research of the toxicity effect mechanisms of heavy metals on freshwater organisms and their water quality criteria in China. Journal of Chemistry, 2020, 1-12. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/9010348
Brinkman, S.F., Johnston, W.D. Acute Toxicity of Zinc to Several Aquatic Species Native to the Rocky Mountains. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 62, 272–281 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-011-9698-3 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-011-9698-3
Kaur, B., Kaur, N., & Kumar, S. (2018). Colorimetric metal ion sensors–a comprehensive review of the years 2011–2016. Coordination chemistry reviews, 358, 13-69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2017.12.002. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2017.12.002
Prodi, L.; Bolletta, F.; Montalti, M.; Zaccheroni, N., Luminescent chemosensors for transition metal ions. Coordination Chemistry Reviews 2000, 205 (1), 59-83. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0010-8545(00)00242-37 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0010-8545(00)00242-3
Trigo-López, M.; Muñoz, A.; Ibeas, S.; Serna, F.; García, F. C.; García, J. M., Colorimetric detection and determination of Fe (III), Co (II), Cu (II) and Sn (II) in aqueous media by acrylic polymers with pendant terpyridine motifs. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 2016, 226, 118-126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.11.116 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.11.116
Obasi, Philip Njoku, and Bennard Benedict Akudinobi. “Potential Health Risk and Levels of Heavy Metals in Water Resources of Lead–Zinc Mining Communities of Abakaliki, Southeast Nigeria”in Applied Water Science,2020, 10 (7): 1–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-020-01233-z. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-020-01233-z
Sommer, I., Fernández, P., Rivas, H., & Gutiérrez, M. E. (2000). La geoestadística como herramienta en estudios de contaminación de suelos. Análisis de caso: afectación de suelo por arsénico, plomo y cadmio contenidos en jales mineros. Revista internacional de contaminación ambiental, 16(4), 205-214.
Hernandez, J., Patino, F., Rivera, I., Reyes, I. A., Flores, M. U., Juarez, J. C., & Reyes, M. (2014). Leaching kinetics in cyanide media of Ag contained in the industrial mining-metallurgical wastes in the state of Hidalgo, Mexico. International Journal of Mining Science and Technology, 24(5), 689-694. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmst.2014.07.003
Alvillo-Rivera, A., Garrido-Hoyos, S., Buitron, G., Thangarasu-Sarasvathi, P., & Rosano-Ortega, G. (2021). Biological treatment for the degradation of cyanide: A review. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 12, 1418-1433. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.03.030
Secretaría de Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales. Dictamen Diagnóstico Ambiental Río Sonora. 28 de septiembre de 2023. Recuperado el 15 de noviembre de 2023 de: https://www.gob.mx/semarnat/documentos/dictamen-diagnostico-ambiental-rio-sonora?state=publishe
Zhang, Meng, Lina Zhang, Huafeng Tian, and Ang Lu. “Universal Preparation of Cellulose-Based Colorimetric Sensor for Heavy Metal Ion Detection” in Carbohydrate Polymers, 2020, vol. 236: 116037. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116037. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116037
Hernández Cruz, A. “Detección Colorimétrica de Metales Potencialmente Tóxicos en Agua por Películas Sensoras (Maestría)”, 2018. Universidad de Sonora.
WHO, Guidelines for drinking-water quality, World Health Organization, 2004. Recuperado el 11 de noviembre de 2023 de: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241549950.
Dorsey, A., & Ingerman, L. (2004). Toxicological profile for copper.
Rubio, C.; González Weller, D.; Martín-Izquierdo, R. E.; Revert, C.; Rodríguez, I.; Hardisson, A., El zinc: oligoelemento esencial. Nutrición Hospitalaria 2007, 22 (1), 101-107.
Olivares Arias, V.; Valverde Som, L.; Quiros Rodríguez, V.; García Romero, R.; Muñoz, N.; Navarro Alarcón, M.; Cabrera Vique, C., Níquel en alimentos y factores influyentes en sus niveles, ingesta, biodisponibilidad y toxicidad: una revisión. CyTA-Journal of Food 2015, 13 (1), 87-101.https://doi.org/10.1080/19476337.2014.917383 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/19476337.2014.917383
Ye, Shuang, Lanlan Li, Yue Ou, Weijia Li, Shu Zhang, Ke Huang, Hong Luo, Zhirong Zou, and Xiaoli Xiong. “In Situ Formation of Silver Nanoparticles via Hydride Generation: A Miniaturized/Portable Visual Colorimetric System for Arsenic Detection in Environmental Water Samples” in Analytica Chimica, 2022, Acta 1192: 339366. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ACA.2021.339366. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2021.339366
Fernandes, Gabriel Martins, Weida R. Silva, Diandra Nunes Barreto, Rafaela S. Lamarca, Paulo Clairmont F. Lima Gomes, João Flávio da S Petruci, and Alex D. Batista. “Novel Approaches for Colorimetric Measurements in Analytical Chemistry – A Review” in Analytica Chimica 2020, Acta 1135 (October): 187–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ACA.2020.07.030 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2020.07.030
Shishkin, Y. L.; Dmitrienko, S. G.; Medvedeva, O. M.; Badakova, S. A.; Pyatkova, L. N., Use of a scanner and digital image-processing software for the quantification of adsorbed substances. Journal of Analytical Chemistry 2004, 59 (2), 102-106. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JANC.0000014733.32082.4b DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JANC.0000014733.32082.4b
Capitán-Vallvey, L. F.; Lopez-Ruiz, N.; Martinez-Olmos, A.; Erenas, M. M.; Palma, A. J., Recent developments in computer vision-based analytical chemistry: A tutorial review. Analytica chimica acta 2015, 899, 23-56. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2015.10.009
Askim, J. R.; Mahmoudi, M.; Suslick, K. S. “Optical sensor arrays for chemical sensing: the optoelectronic nose” in Chemical Society Reviews 2013, 42 (22), 8649-8682. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cs60179j
O. Laatikainen, T. Samarina, P. Haapea, A. Belenikhina, Participatory Monitoring as A Supportive Tool for Better Situational Awareness in Contaminants’ Leakage and Prevention of Environmental Pollution, Procedia Environ. Sci. Eng. Manag. 7 (2020) 131–136.
À. Boso, B. Álvarez, C. Oltra, J. Garrido, C. Muñoz, Á. Hofflinger, Out of sight, out of mind: participatory sensing for monitoring indoor air quality, Environ. Monit. Assess. 192 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-8058-z. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-8058-z
A. Commodore, S. Wilson, O. Muhammad, E. Svendsen, J. Pearce, Community-based participatory research for the study of air pollution: a review of motivations, approaches, and outcomes, Environ. Monit. Assess. 189 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-6063-7. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-6063-7
D. Hasenfratz, O. Saukh, S. Sturzenegger, and L. Thiele, “IPSN’12 - Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Information Processing in Sensor Networks,” IPSN’12 - Proc. 11th Int. Conf. Inf. Process. Sens. Networks, pp. 1–5, 2012.
A. Burgos, R. Páez, E. Carmona, H. Rivas, A systems approach to modeling Community-Based Environmental Monitoring: a case of participatory water quality monitoring in rural Mexico, Environ. Monit. Assess. 185 (2013) 10297–10316. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-013-3333-x
Publicado
Cómo citar
Número
Sección
Licencia
Derechos de autor 2023 EPISTEMUS

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-CompartirIgual 4.0.
La revista adquiere los derechos patrimoniales de los artículos sólo para difusión sin ningún fin de lucro, sin menoscabo de los propios derechos de autoría.
Los autores son los legítimos titulares de los derechos de propiedad intelectual de sus respectivos artículos, y en tal calidad, al enviar sus textos expresan su deseo de colaborar con la Revista Epistemus, editada semestralmente por la Universidad de Sonora.
Por lo anterior, de manera libre, voluntaria y a título gratuito, una vez aceptado el artículo para su publicación, ceden sus derechos a la Universidad de Sonora para que la Universidad de Sonora edite, publique, distribuya y ponga a disposición a través de intranets, internet o CD dicha obra, sin limitación alguna de forma o tiempo, siempre y cuando sea sin fines de lucro y con la obligación expresa de respetar y mencionar el crédito que corresponde a los autores en cualquier utilización que se haga del mismo.
Queda entendido que esta autorización no es una cesión o transmisión de alguno de sus derechos patrimoniales en favor de la mencionada institución. La UniSon le garantiza el derecho de reproducir la contribución por cualquier medio en el cual usted sea el autor, sujeto a que se otorgue el crédito correspondiente a la publicación original de la contribución en Epistemus.
Salvo indicación contraria, todos los contenidos de la edición electrónica se distribuyen bajo una licencia de uso y Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0) Puede consultar desde aquí la versión informativa y el texto legal de la licencia. Esta circunstancia ha de hacerse constar expresamente de esta forma cuando sea necesario.