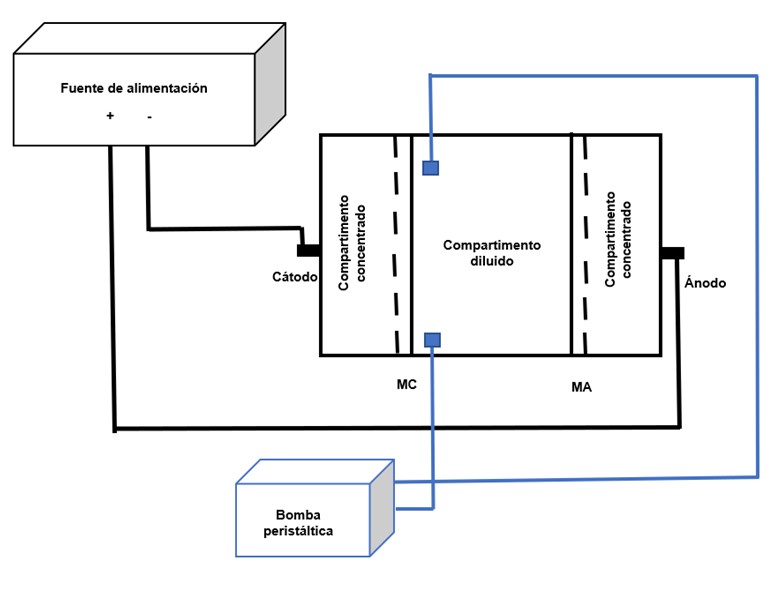
Removal of Zinc from a Synthetic Effluent by Electrodialysis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.36790/epistemus.v17i34.266Keywords:
Electrodyalisis, zinc removal, water trratmentAbstract
Water contamination with heavy metals represents a problem for human health and the environment. Zinc is one of the most common metals in water pollution, which is used in a wide variety of industrial processes. Electrodialysis is an electrochemical technique used for the removal of metal ions, where they are separated from the aqueous solution by a transportation process under the influence of an electric field. It is a promising technique due to its high efficiency and low cost. As the demand for clean water increases, electrodialysis becomes an attractive alternative for contaminant removal, especially in areas where water resources are scarce or where conventional methods are not effective. In this paper, the electrodialysis process and its application in the removal of zinc from water in a synthetic effluent will be described.
Downloads
References
Alvarado, Julio. 2017. “Impactos económicos y sociales de las políticas nacionales mineras en Ecuador (2000-2006)”. Revista de Ciencias Sociales 23 (4): 53-64. DOI: https://www.redalyc.org/articulo.oa?id=28055641005 DOI: https://doi.org/10.31876/rcs.v23i4.25137
Arreola C. y Col., R.M.J.C., Pérez C. R., Martínez G. V.J y Rodríguez R. J., 2020. Electrodiálisis aplicada a la remoción de iones de hierro en un efluente sintético.
Babilas, D. y Dydo, P., 2018. Selective zinc recovery from electroplating wastewaters by electrodialysis enhanced with complex formation. Separation and Purification Technology, 192: 419-428 DOI: https:// doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2017.10.013 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2017.10.013
El-Naas, M. H., Al-Zuhair, S., Alhaija, M. A., & Bashir, M. J. (2015). Removal of zinc ions from aqueous solution using electrodialysis. Desalination and Water Treatment, 53(9), 2429-2439. DOI: 10.1080/19443994.2013.879406
National Center for Biotechnology Information. "Zinc". Fecha de acceso: Feb. 26, 2023. URL: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Zinc
NMX-AA-008-SCFI-2000 Análisis de agua – determinación del pH – método de prueba: Secretaría de Economía. (2000). NMX-AA-008-SCFI-2000 Análisis de agua – determinación del pH – método de prueba. México: Diario Oficial de la Federación.
NMX-AA-051-SCFI-2016. Análisis de agua - Medición de metales por absorción atómica en aguas naturales, potables, residuales y residuales tratadas - Método de prueba. Secretaría de Economía, México. 2016.
Noroozi, R., Ghasemi, M., Ale-Ebrahim, M., & Eikani, M. H. (2018). Electrodialysis for removal of zinc ions from aqueous solutions: Optimization of operating conditions and electrode materials. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 129, 152-162. DOI: 10.1016/j.cherd.2017.11.010 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2017.11.010
SEMARNAT (2021). Norma Oficial Mexicana NOM-001-SEMARNAT-2021, Que establece los límites permisibles de contaminantes en las descargas de aguas residuales en cuerpos receptores propiedad de la nación. DOF (Diario Oficial de la Federación).
Secretaria-de-Economía, 2021. Minería. Acciones y Programas.
Secretaría-de-Economía, 2017. Contexto de México en la Minería.
Secretaría de Economía. (2013). NMX-AA-007-SCFI-2013. Análisis de agua – medición de la temperatura en aguas naturales, residuales y residuales tratadas – método de prueba. Ciudad de México: Diario Oficial de la Federación.
Xiao, C., Yu, S., Xu, L., & Xu, B. (2019). Removal of zinc ion by electrodialysis: Effects of applied voltage and pH. Separation and Purification Technology, 215, 669-677. DOI: 10.1016/j.seppur.2019.01.008 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.01.008
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 EPISTEMUS

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
The magazine acquires the patrimonial rights of the articles only for diffusion without any purpose of profit, without diminishing the own rights of authorship.
The authors are the legitimate owners of the intellectual property rights of their respective articles, and in such quality, by sending their texts they express their desire to collaborate with the Epistemus Magazine, published biannually by the University of Sonora.
Therefore, freely, voluntarily and free of charge, once accepted the article for publication, they give their rights to the University of Sonora for the University of Sonora to edit, publish, distribute and make available through intranets, Internet or CD said work, without any limitation of form or time, as long as it is non-profit and with the express obligation to respect and mention the credit that corresponds to the authors in any use that is made of it.
It is understood that this authorization is not an assignment or transmission of any of your economic rights in favor of the said institution. The University of Sonora guarantees the right to reproduce the contribution by any means in which you are the author, subject to the credit being granted corresponding to the original publication of the contribution in Epistemus.
Unless otherwise indicated, all the contents of the electronic edition are distributed under a license for use and Creative Commons — Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International — (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0) You can consult here the informative version and the legal text of the license. This circumstance must be expressly stated in this way when necessary.
The names and email addresses entered in this journal will be used exclusively for the purposes established in it and will not be provided to third parties or for their use for other purposes.