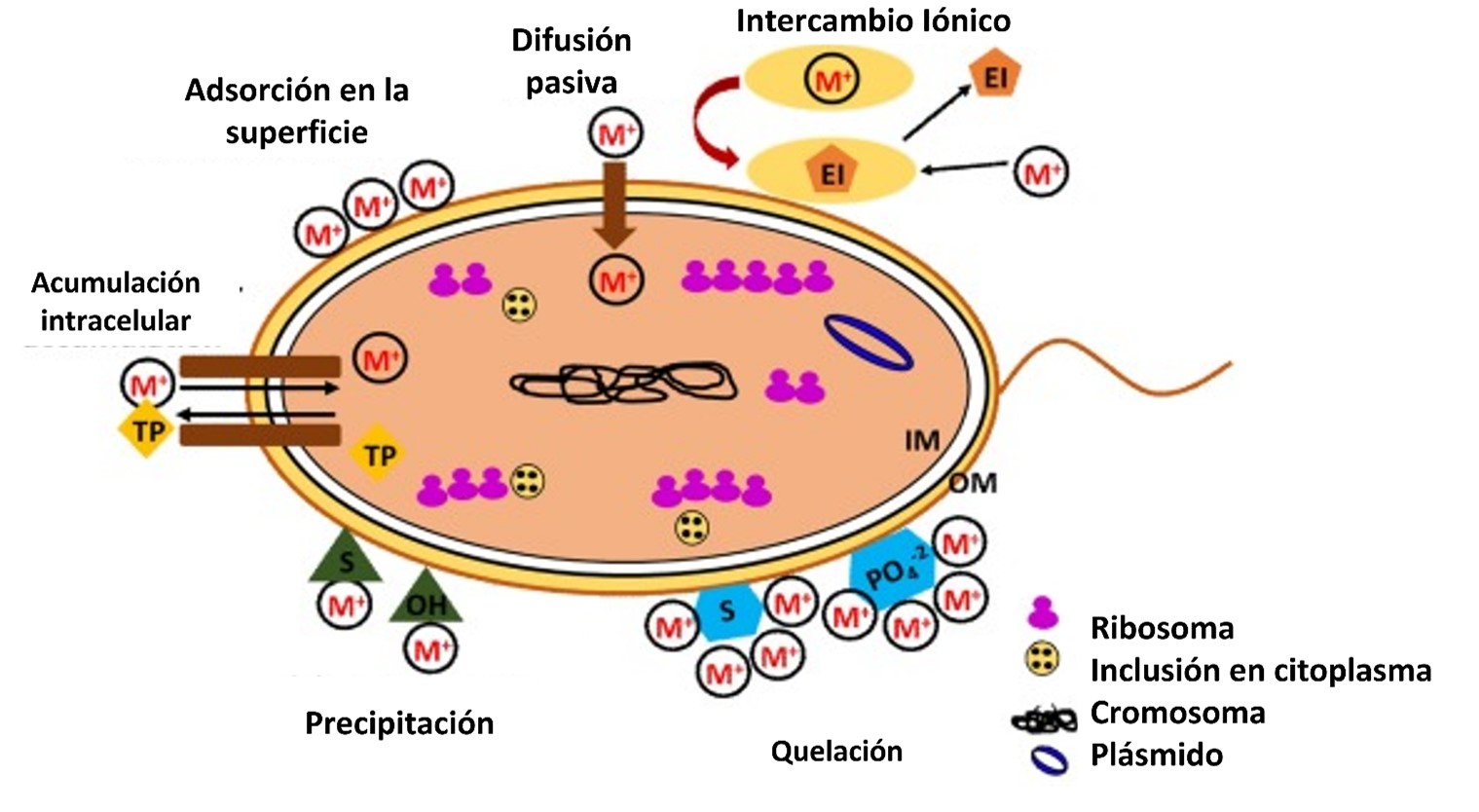
Bacteria Tolerant and Resistant to Heavy Metals in the Environment
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.36790/epistemus.v17i35.287Keywords:
heavy metal, Remediation, bacteriaAbstract
Environmental pollution by heavy metals is largely the result of human activities, particularly the mining industry. The extraction and processing of minerals generates large quantities of toxic compounds that affect the quality of the environment and the health of living beings. For a long time, efforts have been made to develop strategies to remove heavy metals from the environment to mitigate their toxicity. Among these strategies, those that use organisms such as plants, fungi, algae, and bacteria stand out, since they are more efficient, do not generate secondary waste and are not costly. These organisms must have the capacity to grow in high concentrations of metals in order to be used in remediation. In this work seeks to show the different mechanisms used by bacteria for the removal of metals, as well as the metals that can be eliminated.Downloads
References
C. C. Azubuike, C. B. Chikere, and G. C. Okpokwasili, "Bioremediation techniques-classification based on site of application: principles, advantages, limitations and prospects," World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology, vol. 32, no. 11, Nov 2016, Art no. 180, doi: 10.1007/s11274-016-2137-x. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-016-2137-x
K. S. Kumar, H. U. Dahms, E. J. Won, J. S. Lee, and K. H. Shin, "Microalgae - A promising tool for heavy metal remediation," Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, vol. 113, pp. 329-352, Mar 2015, doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.12.019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.12.019
E. I. Valenzuela, A. C. Garcia-Figueroa, L. E. Amabilis-Sosa, F. E. Molina-Freaner, and A. M. Pat-Espadas, "Stabilization of potentially toxic elements contained in mine waste: A microbiological approach for the environmental management of mine tailings," Journal of Environmental Management, vol. 270, Sep 2020, Art no. 110873, doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110873. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110873
R. Loredo-Portales et al., "Mobility and accessibility of Zn, Pb, and As in abandoned mine tailings of northwestern Mexico," Environmental Science and Pollution Research, vol. 27, no. 21, pp. 26605-26620, Jul 2020, doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-09051-1. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09051-1
X. F. Gao, L. Jiang, Y. L. Mao, B. Yao, and P. H. Jiang, "Progress, Challenges, and Perspectives of Bioleaching for Recovering Heavy Metals from Mine Tailings," Adsorption Science & Technology, vol. 2021, May 2021, Art no. 9941979, doi: 10.1155/2021/9941979. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/9941979
M. Gutierrez-Ruiz et al., "Acid spill impact on Sonora River basin. Part I. sediments: Affected area, pollutant geochemistry and health aspects," Journal of Environmental Management, vol. 314, Jul 2022, Art no. 115032, doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.115032. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.115032
J. Helser, E. Vassilieva, and V. Cappuyns, "Environmental and human health risk assessment of sulfidic mine waste: Bioaccessibility, leaching and mineralogy," Journal of Hazardous Materials, vol. 424, Feb 2022, Art no. 127313, doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127313. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127313
M. J. Zhang et al., "Geographical distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals: a case study of mine tailings pond," Chemistry and Ecology, vol. 36, no. 1, pp. 1-15, Jan 2020, doi: 10.1080/02757540.2019.1676420. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/02757540.2019.1676420
M. D. G. Baltazar et al., "Copper biosorption by Rhodococcus erythropolis isolated from the Sossego Mine - PA - Brazil," Journal of Materials Research and Technology-Jmr&T, vol. 8, no. 1, pp. 475-483, Jan-Mar 2019, doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2018.04.006. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2018.04.006
D. W. O'Connell, C. Birkinshaw, and T. F. O'Dwyer, "Heavy metal adsorbents prepared from the modification of cellulose: A review," Bioresource Technology, vol. 99, no. 15, pp. 6709-6724, Oct 2008, doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2008.01.036. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2008.01.036
E. Cavalletti et al., "Copper Effect on Microalgae: Toxicity and Bioremediation Strategies," (in eng), Toxics, vol. 10, no. 9, Sep 06 2022, doi: 10.3390/toxics10090527. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10090527
D. Mani and C. Kumar, "Biotechnological advances in bioremediation of heavy metals contaminated ecosystems: an overview with special reference to phytoremediation," International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, vol. 11, no. 3, pp. 843-872, Apr 2014, doi: 10.1007/s13762-013-0299-8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-013-0299-8
B. Gonzalez-Mendez, R. Webster, R. Loredo-Portales, F. Molina-Freaner, and R. Djellouli, "Distribution of heavy metals polluting the soil near an abandoned mine in Northwestern Mexico," Environmental Earth Sciences, vol. 81, no. 6, Mar 2022, Art no. 176, doi: 10.1007/s12665-022-10285-0. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10285-0
R. Del Rio-Salas et al., "Mineralogy and Geochemistry of Rural Road Dust and Nearby Mine Tailings: A Case of Ignored Pollution Hazard from an Abandoned Mining Site in Semi-arid Zone," Natural Resources Research, vol. 28, no. 4, pp. 1485-1503, Oct 2019, doi: 10.1007/s11053-019-09472-x. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-019-09472-x
P. R. Yaashikaa, P. S. Kumar, S. Jeevanantham, and R. Saravanan, "A review on bioremediation approach for heavy metal detoxification and accumulation in plants," Environmental Pollution, vol. 301, May 2022, Art no. 119035, doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119035. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119035
N. Vaid, J. Sudan, S. Dave, H. Mangla, and H. Pathak, "Insight Into Microbes and Plants Ability for Bioremediation of Heavy Metals," Current Microbiology, vol. 79, no. 5, May 2022, Art no. 141, doi: 10.1007/s00284-022-02829-1. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-022-02829-1
K. Mathivanan, J. U. Chandirika, A. Vinothkanna, H. Yin, X. Liu, and D. Meng, "Bacterial adaptive strategies to cope with metal toxicity in the contaminated environment - A review," (in eng), Ecotoxicol Environ Saf, vol. 226, p. 112863, Dec 15 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112863. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112863
S. Verma and A. Kuila, "Bioremediation of heavy metals by microbial process," Environmental Technology & Innovation, vol. 14, May 2019, Art no. 100369, doi: 10.1016/j.eti.2019.100369. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2019.100369
J. J. Fan, T. O. Okyay, and D. F. Rodrigues, "The synergism of temperature, pH and growth phases on heavy metal biosorption by two environmental isolates," Journal of Hazardous Materials, vol. 279, pp. 236-243, Aug 2014, doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.07.016. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.07.016
D. Kossoff, W. E. Dubbin, M. Alfredsson, S. J. Edwards, M. G. Macklin, and K. A. Hudson-Edwards, "Mine tailings dams: Characteristics, failure, environmental impacts, and remediation," Applied Geochemistry, vol. 51, pp. 229-245, Dec 2014, doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2014.09.010. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2014.09.010
M. Priyadarshanee and S. Das, "Biosorption and removal of toxic heavy metals by metal tolerating bacteria for bioremediation of metal contamination: A comprehensive review," Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, vol. 9, no. 1, Feb 2021, Art no. 104686, doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2020.104686. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104686
P. Gupta and B. Diwan, "Bacterial Exopolysaccharide mediated heavy metal removal: A Review on biosynthesis, mechanism and remediation strategies," (in eng), Biotechnol Rep (Amst), vol. 13, pp. 58-71, Mar 2017, doi: 10.1016/j.btre.2016.12.006. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2016.12.006
T. Kiran Marella, A. Saxena, and A. Tiwari, "Diatom mediated heavy metal remediation: A review," (in eng), Bioresour Technol, vol. 305, p. 123068, Jun 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123068. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123068
O. Monge-Amaya, J. L. Valenzuela-Garcia, E. Acedo-Felix, M. T. Certucha-Barragan, and F. J. Almendariz-Tapia, "Copper biosorption in batch and continuous evaluation using immobilized aerobic bacteria in clinoptilolite," Revista Internacional De Contaminacion Ambiental, vol. 24, no. 3, pp. 107-115, Aug 2008.
J.-L. Zhou, L. Yang, K.-X. Huang, D.-Z. Chen, and F. Gao, "Mechanisms and application of microalgae on removing emerging contaminants from wastewater: A review," Bioresource Technology, vol. 364, p. 128049, 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2022.128049. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2022.128049
M. Nanda, V. Kumar, and D. K. Sharma, "Multimetal tolerance mechanisms in bacteria: The resistance strategies acquired by bacteria that can be exploited to 'clean-up' heavy metal contaminants from water," Aquatic Toxicology, vol. 212, pp. 1-10, Jul 2019, doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2019.04.011. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2019.04.011
A. K. Priya, L. Gnanasekaran, K. Dutta, S. Rajendran, D. Balakrishnan, and M. Soto-Moscoso, "Biosorption of heavy metals by microorganisms: Evaluation of different underlying mechanisms," Chemosphere, vol. 307, Nov 2022, Art no. 135957, doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135957. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135957
A. Choinska-Pulit, J. Sobolczyk-Bednarek, and W. Laba, "Optimization of copper, lead and cadmium biosorption onto newly isolated bacterium using a Box-Behnken design," Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, vol. 149, pp. 275-283, Mar 2018, doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.12.008. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.12.008
A. Elahi, A. Rehman, S. Z. Hussain, S. Zulfiqar, and A. R. Shakoori, "Isolation and characterization of a highly effective bacterium Bacillus cereus b-525k for hexavalent chromium detoxification," Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, vol. 29, no. 4, pp. 2878-2885, Apr 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2022.01.027. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2022.01.027
M. Oves, M. S. Khan, and A. Zaidi, "Biosorption of heavy metals by Bacillus thuringiensis strain OSM29 originating from industrial effluent contaminated north Indian soil," Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, vol. 20, no. 2, pp. 121-129, Apr 2013, doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2012.11.006. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2012.11.006
A. A. Ikhumetse , O. P. Abioye, and S. A. Aransiola, "Biosorption Potential of Bacteria on Lead and Chromium in Groundwater Obtained from Mining Community " Acta Scientific Microbiology, vol. 2, pp. 123-137, 2019, doi: 10.31080/ASMI.2019.02.0252.
D. Li et al., "Discovery of a novel native bacterium of Providencia sp. with high biosorption and oxidation ability of manganese for bioleaching of heavy metal contaminated soils," Chemosphere, vol. 241, Feb 2020, Art no. 125039, doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125039. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125039
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 EPISTEMUS

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
The magazine acquires the patrimonial rights of the articles only for diffusion without any purpose of profit, without diminishing the own rights of authorship.
The authors are the legitimate owners of the intellectual property rights of their respective articles, and in such quality, by sending their texts they express their desire to collaborate with the Epistemus Magazine, published biannually by the University of Sonora.
Therefore, freely, voluntarily and free of charge, once accepted the article for publication, they give their rights to the University of Sonora for the University of Sonora to edit, publish, distribute and make available through intranets, Internet or CD said work, without any limitation of form or time, as long as it is non-profit and with the express obligation to respect and mention the credit that corresponds to the authors in any use that is made of it.
It is understood that this authorization is not an assignment or transmission of any of your economic rights in favor of the said institution. The University of Sonora guarantees the right to reproduce the contribution by any means in which you are the author, subject to the credit being granted corresponding to the original publication of the contribution in Epistemus.
Unless otherwise indicated, all the contents of the electronic edition are distributed under a license for use and Creative Commons — Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International — (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0) You can consult here the informative version and the legal text of the license. This circumstance must be expressly stated in this way when necessary.
The names and email addresses entered in this journal will be used exclusively for the purposes established in it and will not be provided to third parties or for their use for other purposes.