Holography and Mathematics
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.36790/epistemus.v18i37.367Keywords:
Hologram, laser light, wave equation, Kirchhoff solution, stationary phaseAbstract
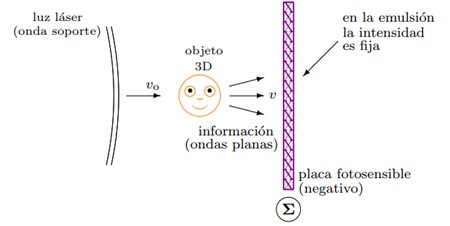
The general objective of this paper is to analyze mathematically the physical process of reproduction of a transmission hologram, in order to contrast directly observable results with approximations obtained theoretically. On one hand, when observing a hologram, a region is located on it where a three-dimensional object is faithfully reproduced using a special photographic technique called holography. On the other hand, by applying a simple mathematical model to describe this fact, through the well-known classical wave equation —with a solution given in Kirchhoff form, which is analyzed using an asymptotic method of complex analysis— an approximate result is obtained that allows for a congruent conclusion about this particular process.
Downloads
References
[[1] P.R. Garabedian. Partial Differential Equations. Chelsea Publishing Co., 1986. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-044375-8.50016-2
G. Saxby. Practical Holography. Boca Raton, Florida: IoP Publishing, 2004.
Disponible en https://doi.org/10.1201/9781420033663 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1201/9781420033663
H.M. Smith. Principles of Holography. Nueva York: John Wiley & Sons, 1979.
R. Flores-Espinoza y R. González-González. Temas y Problemas Selectos de Análisis Matemático. Teoremas de Existencia y Aplicaciones. Hermosillo, Sonora: Universidad de Sonora, 2022.
Disponible en https://doi.org/10.47807/UNISON.95 DOI: https://doi.org/10.47807/UNISON.95
J.E. Marsden. Elementary Classical Analysis. San Francisco: W.H Freeman and Company, 1974.
M.G. García y R. González-González. Notas de Cálculo Vectorial. Hermosillo, Sonora: Universidad de Sonora, 2019.
Disponible en https://www.mat.uson.mx/sitio/documentos/libros/Notas_Calculo_Vectorial.pdf
G.B. Arfken. Mathematical Methods for Physicists, 3.a ed. Orlando: Academic Press,1985.
Disponible en https://doi.org/10.1016/C2013-0-10310-8 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/C2013-0-10310-8
R. Courant y D. Hilbert. Methods of Mathematical Physics: Vol. II. Partial Differential Equations. Interscience Publishers, 1965.
J.W. Dettman. Applied Complex Variables. Nueva York: Dover Publications, 1984.
A. Erdelyi. Asymptotic Expansions. Dover Publications, 1956. DOI: https://doi.org/10.21236/AD0055660
B. Friedman. Lectures on Applications-Oriented Mathematics. Nueva York: John Wiley & Sons, 1991. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118033111
J.P. Keener. Principles of Applied Mathematics. Transformation and Approximation.
Addison-Wesley, 1988.
Disponible en https://doi.org/10.2307/3618500 DOI: https://doi.org/10.2307/3618500
E. Mihaylova. Holography–Basic Principles and Contemporary Applications.
InTech DTP, 2013.
Disponible en http://dx.doi.org/10.5772/46111 DOI: https://doi.org/10.5772/46111
I. Stakgold. Green's Functions and Boundary Value Problems. Nueva York: John Wiley & Sons, 1979.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 EPISTEMUS

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
The magazine acquires the patrimonial rights of the articles only for diffusion without any purpose of profit, without diminishing the own rights of authorship.
The authors are the legitimate owners of the intellectual property rights of their respective articles, and in such quality, by sending their texts they express their desire to collaborate with the Epistemus Magazine, published biannually by the University of Sonora.
Therefore, freely, voluntarily and free of charge, once accepted the article for publication, they give their rights to the University of Sonora for the University of Sonora to edit, publish, distribute and make available through intranets, Internet or CD said work, without any limitation of form or time, as long as it is non-profit and with the express obligation to respect and mention the credit that corresponds to the authors in any use that is made of it.
It is understood that this authorization is not an assignment or transmission of any of your economic rights in favor of the said institution. The University of Sonora guarantees the right to reproduce the contribution by any means in which you are the author, subject to the credit being granted corresponding to the original publication of the contribution in Epistemus.
Unless otherwise indicated, all the contents of the electronic edition are distributed under a license for use and Creative Commons — Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International — (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0) You can consult here the informative version and the legal text of the license. This circumstance must be expressly stated in this way when necessary.
The names and email addresses entered in this journal will be used exclusively for the purposes established in it and will not be provided to third parties or for their use for other purposes.