Synthesis of iron oxides as precursors for zinc ferrite
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.36790/epistemus.v18i37.373Keywords:
Zinc Ferrite, Chemical Coprecipitation, Mechanical GrindingAbstract
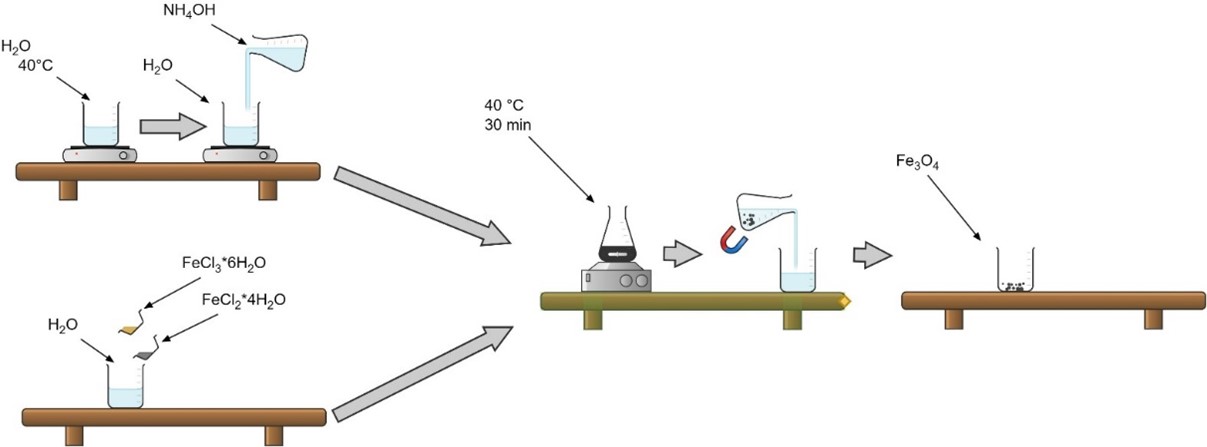
Ferrites are materials with multiple applications due to their unique magnetic properties. For this investigation, magnetite (Fe3O4) particles were synthesized by chemical co-precipitation by varying the temperature of the medium. From magnetite, maghemite (Fe2O3) was synthesized by applying a thermal treatment. Magnetite and maghemite were used along with reactive- grade zinc oxide (ZnO) particles as precursors for the synthesis of zinc ferrite (ZnFe2O4) particles by the mechanical grinding technique. During the grinding, the grinding speed and composition of the precursors varied. Finally, the zinc ferrite samples were given post-grinding thermal treatment. Mechanical grinding assisted by thermal treatment proved to be the most effective in the synthesis of zinc ferrite particles. The synthesized samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction for analysis using the Match software.
Downloads
References
M. A. Díaz-Solís, J. Hernández-Torres, y L. Zamora-Peredo, “Estudio por espectroscopía Raman del efecto del tiempo de anodización en nanovarillas de hidróxido de cobre”, Nova Scientia, vol. 14, núm. 28, abr. 2022, doi: 10.21640/ns.v14i28.2901. DOI: https://doi.org/10.21640/ns.v14i28.2901
G. Bolivar, “Óxido de hierro”, My Research Folder. [En línea]. Disponible en: https://www.lifeder.com/oxido-de-hierro/
L. Yang et al., “Sensitive contrast-hnhanced magnetic resonance imaging of orthotopic and metastatic hepatic tumors by ultralow doses of zinc ferrite octapods”, Chemistry of Materials, vol. 31, núm. 4, pp. 1381–1390, feb. 2019, doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.8b04760. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.8b04760
Y. Wang et al., “Engineering ferrite nanoparticles with enhanced magnetic response for advanced biomedical applications”, Mater Today Adv, vol. 8, dic. 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.mtadv.2020.100119. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtadv.2020.100119
R. Ramadan, “Physical study of cobalt ferrite and its application in purification of water”, Appl Phys A Mater Sci Process, vol. 125, núm. 12, dic. 2019, doi: 10.1007/s00339-019-3121-8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-3121-8
F. Zhang, Z. Su, F. Wen, y F. Li, “Synthesis and characterization of polystyrene-grafted magnetite nanoparticles”, Colloid Polym Sci, vol. 286, núm. 6–7, pp. 837–841, jun. 2008, doi: 10.1007/s00396-008-1854-6. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-008-1854-6
A. H. Lu, E. L. Salabas, y F. Schüth, “Magnetic nanoparticles: Synthesis, protection, functionalization, and application”, 2007. doi: 10.1002/anie.200602866. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200602866
E. M. García-Rosales, Ma. G. Rosales-Sosa, J. C. Ríos-Hurtado, M. García-Yregoi, y B. I. Rosales-Sosa, “Síntesis de ferritas con diferentes proporciones Zn/Fe mediante coprecipitación química y efecto de tratamientos térmicos y molienda mecánica sobre el tamaño de cristalita.”, CienciAcierta, núm. 66, Monclova, pp. 26–40, el 19 de febrero de 2021.
F. Morales, V. Sagredo, T. Torres, y G. Márquez, “Caracterización de nanopartículas de magnetita sintetizadas por el método de coprecipitación”, Revista Ciencia e Ingeniería, vol. 40, núm. 1, pp. 39–44, 2019.
C. Suryanarayana, “Mechanical alloying and milling”, Metals and Materials, vol. 5, núm. 2, Idaho Falls, pp. 121–128, 1999. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6425(99)00010-9. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0079-6425(99)00010-9
Ma. G. Rosales-Sosa, “Nanoferrita de zinc con propiedades morfológicas y estructurales obtenida por coprecipitación química y molienda mecánica”, Tesis Doctoral, Universidad Centro Panamericano de estudios superiores, Monclova, 2020.
R. E. Luque-Álvarez, “Síntesis y caracterización de nanopartículas de ferritas con diferente proporción de zinc/hierro para aplicaciones medioambientales”, Tesis Doctoral, Universidad Nacional de San Agustín de Arequipa, Arequipa- Perú, 2023.
R. L. Palomino, A. M. Bolarín Miró, F. N. Tenorio, F. Sánchez De Jesús, C. A. Cortés Escobedo, y S. Ammar, “Sonochemical assisted synthesis of SrFe12O19 nanoparticles”, Ultrason Sonochem, vol. 29, pp. 470–475, mar. 2016, doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2015.10.023. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2015.10.023
S. Aliramaji, A. Zamanian, y Z. Sohrabijam, “Characterization and Synthesis of Magnetite Nanoparticles by Innovative Sonochemical Method”, Procedia Materials Science, vol. 11, pp. 265–269, 2015, doi: 10.1016/j.mspro.2015.11.022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mspro.2015.11.022
D. Alvear, S. Galeas, V. H. Guerrero, y A. Debut, “Síntesis y Caracterización de Nanopartículas de Magnetita”, Revista Politécnica , vol. 39, núm. 02, jul. 2017.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 EPISTEMUS

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
The magazine acquires the patrimonial rights of the articles only for diffusion without any purpose of profit, without diminishing the own rights of authorship.
The authors are the legitimate owners of the intellectual property rights of their respective articles, and in such quality, by sending their texts they express their desire to collaborate with the Epistemus Magazine, published biannually by the University of Sonora.
Therefore, freely, voluntarily and free of charge, once accepted the article for publication, they give their rights to the University of Sonora for the University of Sonora to edit, publish, distribute and make available through intranets, Internet or CD said work, without any limitation of form or time, as long as it is non-profit and with the express obligation to respect and mention the credit that corresponds to the authors in any use that is made of it.
It is understood that this authorization is not an assignment or transmission of any of your economic rights in favor of the said institution. The University of Sonora guarantees the right to reproduce the contribution by any means in which you are the author, subject to the credit being granted corresponding to the original publication of the contribution in Epistemus.
Unless otherwise indicated, all the contents of the electronic edition are distributed under a license for use and Creative Commons — Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International — (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0) You can consult here the informative version and the legal text of the license. This circumstance must be expressly stated in this way when necessary.
The names and email addresses entered in this journal will be used exclusively for the purposes established in it and will not be provided to third parties or for their use for other purposes.