Analysis of PM2.5 Suspended in Northwest Hermosillo.
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.36790/epistemus.v19i38.410Keywords:
Air Quality, PM2.5, Stationarity, PredictionAbstract
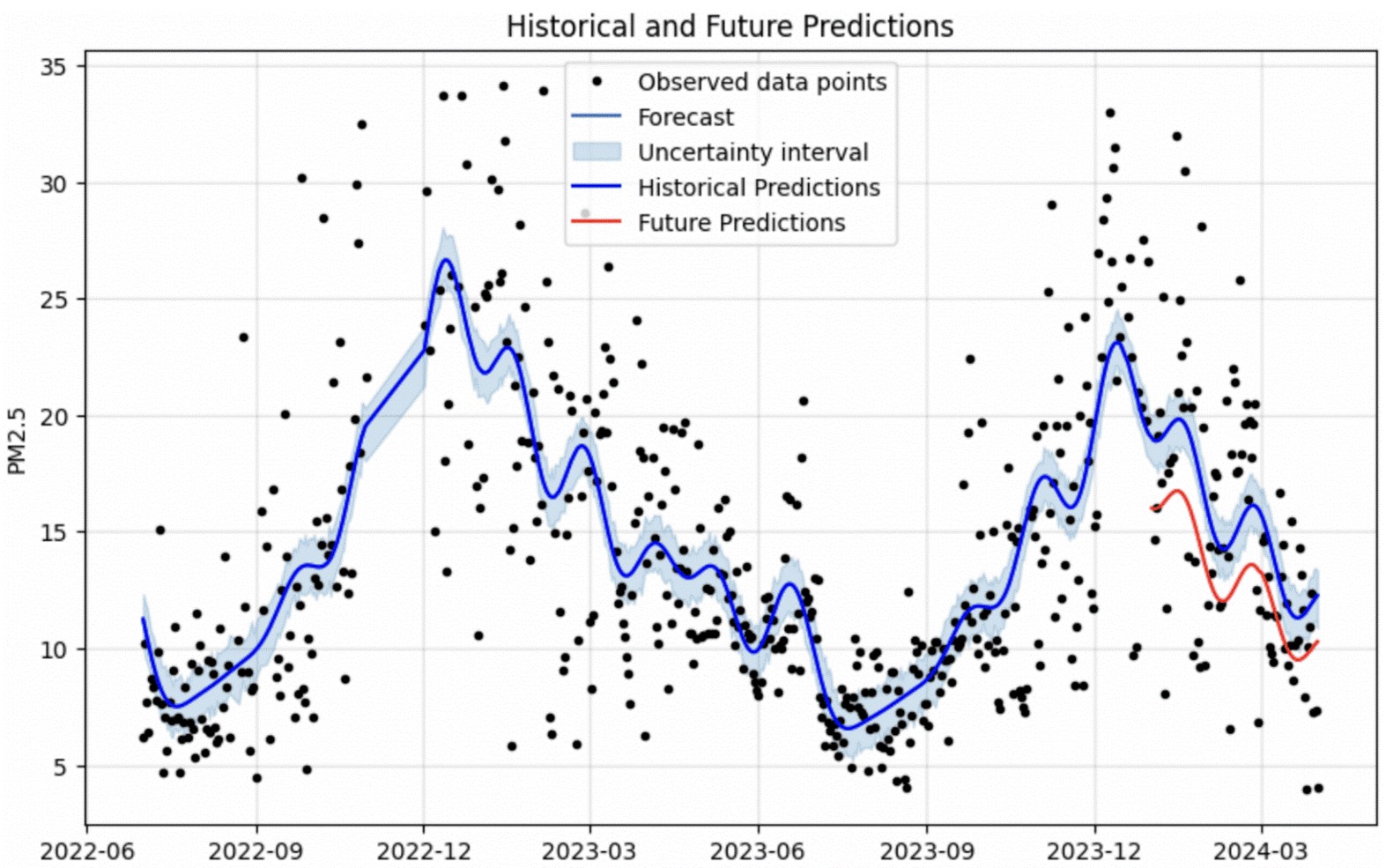
In Hermosillo, Sonora city, low-cost sensors have been used to capture data on PM2.5 particle pollution and other atmospheric pollutants. Since these pollutants have been studied over the past decades, it is essential to predict their future behavior. This study uses machine learning models for predicting and analyzing trends in PM2.5 levels. Preliminary results indicate that pollutant concentrations show clear seasonal variability.
The proposed methodology follows a systematic approach for data preparation and analysis in the context of machine learning algorithms. This approach includes processes such as cleaning, exploration, handling outliers and missing values, scaling categorical data, feature selection, and partitioning the data into training and testing sets.
Downloads
References
D. Meza-Figueroa. «Heavy metal distribution in dust from elementary schools in Hermosillo, Sonora, México». Atmospheric Environment, 2007, 276-28. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2006.08.034
A. Santos Romo. Evaluation of air quality for PM10, NO× and SO2 suspended particles in the city of Hermosillo, Sonora, 2006.
M. E. Cruz Campas, A. Gómez Alvarez, Quintero Núñez, M., y Varela Salazar, J. (2013). «Evaluación de la calidad del aire respecto de partículas suspendidas totales (PST) y metales pesados (Pb, Cd, Ni, Cu, Cr) en la ciudad de Hermosillo, Sonora, México, durante un periodo anual». Revista internacional de contaminación ambiental, 29(4), 269-283.
S. Zhou, W. Wang, L. Zhu, Q. Qiao, y Y. Kang, «Deep-learning architecture for PM2. 5 concentration prediction: A review», Environmental Science and Ecotechnology, 100400, 2024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ese.2024.100400 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ese.2024.100400
U. A. Bhatti, Y. Yan, M. Zhou, S. Ali, A. Hussain, H. Qingsong, y L. Yuan, «Time series analysis and forecasting of air pollution particulate matter (PM 2.5): an SARIMA and factor analysis approach», Ieee Access, 9, 41019-41031, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3060744 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3060744
F. Mohammadi, H. Teiri, Y. Hajizadeh, A. Abdolahnejad, y A. Ebrahimi, «Prediction of atmospheric PM2. 5 level by machine learning techniques in Isfahan, Iran», Scientific Reports, 14(1), 2109, 2024. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-52617-z DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-52617-z
U. Pak, J. Ma, U. Ryu K. Ryom, U. Juhyok, K. Pak, y C. Pak, «Deep learning-based PM2. 5 prediction considering the spatiotemporal correlations: A case study of Beijing, China», Science of the Total Environment, 699, 133561, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.07.367 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.07.367
F. Xiao, M. Yang, H. Fan, G. Fan, y M. A. Al-Qaness, «An improved deep learning model for predicting daily PM2. 5 concentration», Scientific reports, 10(1), 20988, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-77757-w DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-77757-w
H. Jin, X. Chen, R. Zhong, y M. Liu, «Influence and prediction of PM2. 5 through multiple environmental variables in China», Science of The Total Environment, 849, 157910, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.157910 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.157910
Q. Xiao, G. Geng, J. Cheng, F. Liang, R. Li, X. Meng, y K. He, «Evaluation of gap-filling approaches in satellite-based daily PM2. 5 prediction models», Atmospheric Environment, 244, 117921. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2020.117921 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2020.117921
W. Ban y L. Shen, «PM2. 5 prediction based on the CEEMDAN algorithm and a machine learning hybrid model», Sustainability, 14(23), 16128, 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142316128 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/su142316128
Y. C. Chen y D. C. Li, «Selection of key features for PM2. 5 prediction using a wavelet model and RBF-LSTM», Applied Intelligence, 51, 2534-2555, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-020-02031-5 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-020-02031-5
J. Ma, Z. Yu, Y. Qu, J. Xu, y Y. Cao, «Application of the XGBoost machine learning method in PM2. 5 prediction: a case study of Shanghai», Aerosol and Air Quality Research, 20(1), 2020, pp. 128-138. https://doi.org/10.4209/aaqr.2019.08.0408 DOI: https://doi.org/10.4209/aaqr.2019.08.0408
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 EPISTEMUS

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
The magazine acquires the patrimonial rights of the articles only for diffusion without any purpose of profit, without diminishing the own rights of authorship.
The authors are the legitimate owners of the intellectual property rights of their respective articles, and in such quality, by sending their texts they express their desire to collaborate with the Epistemus Magazine, published biannually by the University of Sonora.
Therefore, freely, voluntarily and free of charge, once accepted the article for publication, they give their rights to the University of Sonora for the University of Sonora to edit, publish, distribute and make available through intranets, Internet or CD said work, without any limitation of form or time, as long as it is non-profit and with the express obligation to respect and mention the credit that corresponds to the authors in any use that is made of it.
It is understood that this authorization is not an assignment or transmission of any of your economic rights in favor of the said institution. The University of Sonora guarantees the right to reproduce the contribution by any means in which you are the author, subject to the credit being granted corresponding to the original publication of the contribution in Epistemus.
Unless otherwise indicated, all the contents of the electronic edition are distributed under a license for use and Creative Commons — Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International — (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0) You can consult here the informative version and the legal text of the license. This circumstance must be expressly stated in this way when necessary.
The names and email addresses entered in this journal will be used exclusively for the purposes established in it and will not be provided to third parties or for their use for other purposes.