Agroindustrial Residues as Sources of Nutrients and Phenolic Compounds
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.36790/epistemus.v17i34.265Keywords:
waste food, nutrients, phenolic compoundsAbstract
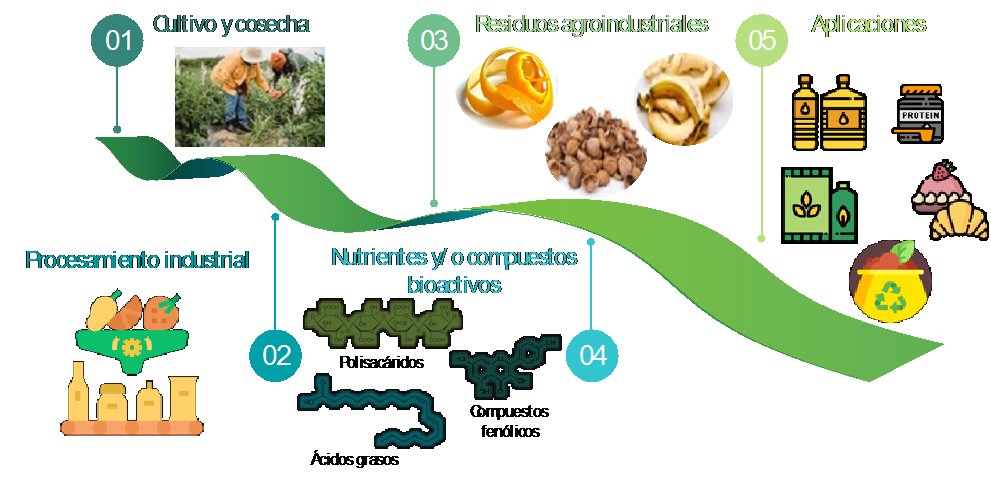
The present work describes the nutrients and phenolic compounds contained in diverse agroindustrial residues (AIR). The AIR could derive in problems that compromise the nutrition and health of the most vulnerable populations if they are not properly used. Therefore, it is important to create alternatives that contribute to counteract the problem, from food production to the consumer's table. AIR from fruits, vegetables, cereals and oilseeds contain nutrients and phenolic compounds that can be beneficial to health, due to their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and antidiabetic effects, among others. The AIR could also be used in food development, due to their techno-functional characteristics such as the capability to act as gelling, emulsifying, stabilizing, and thickening agents. Accordingly, a second use of AIR is promising, however, there are still some challenges to be solved, such as process scaling and optimizing its extraction.
Downloads
References
M. C. Boliko, “FAO and the Situation of Food Security and Nutrition in the World,” J Nutr Sci Vitaminol, vol. 65, no. Supplement, pp. S4–S8, Oct. 2019, doi: 10.3177/jnsv.65.S4. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3177/jnsv.65.S4
Raúl Benítez, “Pérdidas y desperdicios de alimentos en América Latina y el Caribe,” Oficina Regional de la FAO para América Latina y el Caribe, 2015. https://www.fao.org/americas/noticias/ver/es/c/239393/
Z. Usmani et al., “Minimizing hazardous impact of food waste in a circular economy – Advances in resource recovery through green strategies,” Journal of Hazardous Materials, vol. 416, p. 126154, Aug. 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126154. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126154
FAO, “Objetivos de Desarrollo Sostenible,” 2015. https://www.fao.org/sustainable-development-goals/overview/es/
A. Fernandez et al., “Clean recovery of phenolic compounds, pyro-gasification thermokinetics, and bioenergy potential of spent agro-industrial bio-wastes,” Biomass Conv. Bioref., Jan. 2022, doi: 10.1007/s13399-021-02197-z. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-021-02197-z
P. Leite, C. Silva, J. M. Salgado, and I. Belo, “Simultaneous production of lignocellulolytic enzymes and extraction of antioxidant compounds by solid-state fermentation of agro-industrial wastes,” Industrial Crops and Products, vol. 137, pp. 315–322, Oct. 2019, doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2019.04.044. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2019.04.044
B. H. Belmonte-Herrera et al., “Lesser-Consumed Tropical Fruits and Their by-Products: Phytochemical Content and Their Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Potential,” Nutrients, vol. 14, no. 17, p. 3663, Sep. 2022, doi: 10.3390/nu14173663. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14173663
N. J. Salazar-López et al., “Single-Cell Protein Production as a Strategy to Reincorporate Food Waste and Agro By-Products Back intothe Processing Chain,” p. 13, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9110623
R. Bhat, “Sustainability challenges in the valorization of agri-food wastes and by-products,” in Valorization of Agri-Food Wastes and By-Products: Recent Trends, Innovations and Sustainability Challenges, R. Bhat, Ed. 2021, pp. 1–28. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-824044-1.00042-8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-824044-1.00022-2
N. Jiménez-Moreno, I. Esparza, F. Bimbela, L. M. Gandía, and C. Ancín-Azpilicueta, “Valorization of selected fruit and vegetable wastes as bioactive compounds: Opportunities and challenges,” Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, vol. 50, no. 20, pp. 2061–2108, 2020, doi: 10.1080/10643389.2019.1694819. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2019.1694819
C. A. Can-Cauich et al., “Tropical fruit peel powders as functional ingredients: Evaluation of their bioactive compounds and antioxidant activity,” Journal of Functional Foods, vol. 37, pp. 501–506, Oct. 2017, doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2017.08.028. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2017.08.028
N. J. Salazar-López et al., “Avocado fruit and by-products as potential sources of bioactive compounds,” Food Research International, vol. 138, p. 109774, Dec. 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109774. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109774
V. Saraswaty, C. Risdian, I. Primadona, R. Andriyani, D. G. S. Andayani, and T. Mozef, “Pineapple peel wastes as a potential source of antioxidant compounds,” IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ. Sci., vol. 60, p. 012013, Mar. 2017, doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/60/1/012013. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/60/1/012013
N. J. Salazar-López, M. L. Salmerón-Ruiz, J. A. Domínguez-Avila, M. A. Villegas-Ochoa, J. F. Ayala-Zavala, and G. A. González-Aguilar, “Phenolic compounds from ‘Hass’ avocado peel are retained in the indigestible fraction after an in vitro gastrointestinal digestion,” Food Measure, vol. 15, no. 2, pp. 1982–1990, Apr. 2021, doi: 10.1007/s11694-020-00794-6. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-020-00794-6
D. I. L. Gil-López et al., “Production of dietary fibers from sugarcane bagasse and sugarcane tops using microwave-assisted alkaline treatments,” Industrial Crops and Products, vol. 135, pp. 159–169, Sep. 2019, doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2019.04.042. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2019.04.042
S. A. Monteiro, M. M. Barbosa, F. F. Maia da Silva, R. F. Bezerra, and K. da Silva Maia, “Preparation, phytochemical and bromatological evaluation of flour obtained from the acerola (Malpighia punicifolia) agroindustrial residue with potential use as fiber source,” Lwt, vol. 134, pp. 1–7, 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2020.110142. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2020.110142
P. D. Pathak, S. A. Mandavgane, N. M. Puranik, S. J. Jambhulkar, and B. D. Kulkarni, “Valorization of potato peel: a biorefinery approach,” Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, vol. 38, no. 2, pp. 218–230, Feb. 2018, doi: 10.1080/07388551.2017.1331337. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/07388551.2017.1331337
P. D. G. Pacheco, M. A. Baller, F. M. Peres, É. de M. Ribeiro, T. C. Putarov, and A. C. Carciofi, “Citrus pulp and orange fiber as dietary fiber sources for dogs,” Animal Feed Science and Technology, vol. 282, p. 115123, Dec. 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2021.115123. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2021.115123
I. Mármol et al., “Valorization of agro-food by-products and their potential therapeutic applications,” Food and Bioproducts Processing, vol. 128, pp. 247–258, Jul. 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.fbp.2021.06.003. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbp.2021.06.003
M. Kazemi, F. Khodaiyan, M. Labbafi, and S. S. Hosseini, “Ultrasonic and heating extraction of pistachio by-product pectin: physicochemical, structural characterization and functional measurement,” Food Measure, vol. 14, no. 2, pp. 679–693, Apr. 2020, doi: 10.1007/s11694-019-00315-0. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-019-00315-0
P. Lasunon and N. Sengkhamparn, “Effect of ultrasound-assisted, microwave-assisted and ultrasound-microwave-assisted extraction of pectin extraction from industrial tomato waste,” Molecules, vol. 27, no. 1157, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27041157
L. X. López-Martínez, S. A. Enríquez-Valencia, and G. González Aguilar, “Tropical fruits and by-products as a potential source of bioactive polysaccharides: Bioactive polysaccharides from tropical fruits,” BIOTECNIA, vol. 23, no. 3, Oct. 2021, doi: 10.18633/biotecnia.v23i3.1450. DOI: https://doi.org/10.18633/biotecnia.v23i3.1450
I. Benítez-Cortés, A. Pérez-Martínez, R. Álvarez, O. Collado-García, and Y. González-Díaz, “Perspectivas de la producción de inulina a partir de la tuna (Opuntia ficus-indica),” Tecnología Química, vol. 35, no. 2, p. 12, May 2015.
Z. Zeaiter, M. E. Regonesi, S. Cavini, M. Labra, G. Sello, and P. Di Gennaro, “Extraction and Characterization of Inulin-Type Fructans from Artichoke Wastes and Their Effect on the Growth of Intestinal Bacteria Associated with Health,” BioMed Research International, vol. 2019, pp. 1–8, Sep. 2019, doi: 10.1155/2019/1083952. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/1083952
R. Fan, G. Mao, H. Xia, and J. Zeng, “Chemical elucidation and rheological properties of a pectic polysaccharide extracted from Citrus medica L. fruit residues by gradient ethanol precipitation,” International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, vol. 198, pp. 46–53, Feb. 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.12.131. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.12.131
M. Hadidi et al., “Polysaccharides from pineapple core as a canning by-product: Extraction optimization, chemical structure, antioxidant and functional properties,” International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, vol. 163, pp. 2357–2364, Nov. 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.09.092. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.09.092
A. Ritala, S. T. Häkkinen, M. Toivari, and M. G. Wiebe, “Single Cell Protein—State-of-the-Art, Industrial Landscape and Patents 2001–2016,” Front. Microbiol., vol. 8, p. 2009, Oct. 2017, doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.02009. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.02009
S. Smetana, A. Mathys, A. Knoch, and V. Heinz, “Meat alternatives: life cycle assessment of most known meat substitutes,” Int J Life Cycle Assess, vol. 20, no. 9, pp. 1254–1267, Sep. 2015, doi: 10.1007/s11367-015-0931-6. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11367-015-0931-6
C. van der Weele, P. Feindt, A. Jan van der Goot, B. van Mierlo, and M. van Boekel, “Meat alternatives: an integrative comparison,” Trends in Food Science & Technology, vol. 88, pp. 505–512, Jun. 2019, doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2019.04.018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2019.04.018
H. Kamal, C. F. Le, A. M. Salter, and A. Ali, “Extraction of protein from food waste: An overview of current status and opportunities,” Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, vol. 20, no. 3, pp. 2455–2475, May 2021, doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12739. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/1541-4337.12739
M. Peydayesh, M. Bagnani, W. L. Soon, and R. Mezzenga, “Turning Food Protein Waste into Sustainable Technologies,” Chem. Rev., p. acs.chemrev.2c00236, Jun. 2022, doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.2c00236. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.2c00236
A. Tropea, A. Ferracane, A. Albergamo, A. G. Potortì, V. Lo Turco, and G. Di Bella, “Single Cell Protein Production through Multi Food-Waste Substrate Fermentation,” Fermentation, vol. 8, no. 3, p. 91, Feb. 2022, doi: 10.3390/fermentation8030091. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8030091
P. Thiviya, A. Gamage, R. Kapilan, O. Merah, and T. Madhujith, “Single Cell Protein Production Using Different Fruit Waste: A Review,” Separations, vol. 9, no. 7, p. 178, Jul. 2022, doi: 10.3390/separations9070178. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9070178
B. Matthäus and M. Musazcan Özcan, “Oil Content, Fatty Acid Composition and Distributions of Vitamin-E-Active Compounds of Some Fruit Seed Oils,” Antioxidants, vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 124–133, Jan. 2015, doi: 10.3390/antiox4010124. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox4010124
K. L. Alharbi, J. Raman, and H.-J. Shin, “Date Fruit and Seed in Nutricosmetics,” Cosmetics, vol. 8, no. 3, p. 59, Jun. 2021, doi: 10.3390/cosmetics8030059. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics8030059
P. Górnaś and M. Rudzińska, “Seeds recovered from industry by-products of nine fruit species with a high potential utility as a source of unconventional oil for biodiesel and cosmetic and pharmaceutical sectors,” Industrial Crops and Products, vol. 83, pp. 329–338, May 2016, doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.01.021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.01.021
R. G. Araújo, R. M. Rodriguez-Jasso, H. A. Ruiz, M. M. E. Pintado, and C. N. Aguilar, “Avocado by-products: Nutritional and functional properties,” Trends in Food Science & Technology, vol. 80, pp. 51–60, Oct. 2018, doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2018.07.027. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2018.07.027
E. Yilmaz and B. A. Güneşer, “Cold pressed versus solvent extracted lemon (Citrus limon L.) seed oils: yield and properties,” J Food Sci Technol, vol. 54, no. 7, pp. 1891–1900, Jun. 2017, doi: 10.1007/s13197-017-2622-8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-017-2622-8
E. Alves, A. Simoes, and M. R. Domingues, “Fruit seeds and their oils as promising sources of value-added lipids from agro-industrial byproducts: oil content, lipid composition, lipid analysis, biological activity and potential biotechnological applications,” Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, vol. 61, no. 8, pp. 1305–1339, Apr. 2021, doi: 10.1080/10408398.2020.1757617. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2020.1757617
I. M. Martins et al., “Tannase enhances the anti-inflammatory effect of grape pomace in Caco-2 cells treated with IL-1β,” Journal of Functional Foods, vol. 29, pp. 69–76, Feb. 2017, doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2016.12.011. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2016.12.011
K. Kumar, A. N. Yadav, V. Kumar, P. Vyas, and H. S. Dhaliwal, “Food waste: a potential bioresource for extraction of nutraceuticals and bioactive compounds,” Bioresour. Bioprocess., vol. 4, no. 1, p. 18, Dec. 2017, doi: 10.1186/s40643-017-0148-6. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40643-017-0148-6
P. A. R. Fernandes et al., “Apple Pomace Extract as a Sustainable Food Ingredient,” Antioxidants, vol. 8, no. 6, p. 189, Jun. 2019, doi: 10.3390/antiox8060189. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8060189
F. Chaudhry et al., “Extraction and Evaluation of the Antimicrobial Activity of Polyphenols from Banana Peels Employing Different Extraction Techniques,” Separations, vol. 9, no. 7, p. 165, Jun. 2022, doi: 10.3390/separations9070165. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9070165
V. Manasa, A. Padmanabhan, and K. A. Anu Appaiah, “Utilization of coffee pulp waste for rapid recovery of pectin and polyphenols for sustainable material recycle,” Waste Management, vol. 120, pp. 762–771, Feb. 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2020.10.045. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2020.10.045
F. Correddu et al., “Can Agro-Industrial By-Products Rich in Polyphenols be Advantageously Used in the Feeding and Nutrition of Dairy Small Ruminants?,” Animals, vol. 10, no. 1, p. 131, Jan. 2020, doi: 10.3390/ani10010131. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10010131
B. R. Min, T. N. Barry, G. T. Attwood, and W. C. McNabb, “The effect of condensed tannins on the nutrition and health of ruminants fed fresh temperate forages: a review,” Animal Feed Science and Technology, vol. 106, no. 1–4, pp. 3–19, Apr. 2003, doi: 10.1016/S0377-8401(03)00041-5. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0377-8401(03)00041-5
S. A. Salami et al., “Sustainability of feeding plant by-products: A review of the implications for ruminant meat production,” Animal Feed Science and Technology, vol. 251, pp. 37–55, May 2019, doi: 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2019.02.006. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2019.02.006
K. M. Valadez-García et al., “Ferulic acid in animal feeding: Mechanisms of action, productive benefits, and future perspectives in meat production,” Food Bioscience, vol. 43, p. 101247, Oct. 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2021.101247. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbio.2021.101247
A. Görgüç, P. Özer, and F. M. Yılmaz, “Microwave‐assisted enzymatic extraction of plant protein with antioxidant compounds from the food waste sesame bran: Comparative optimization study and identification of metabolomics using LC/Q‐TOF/MS,” J Food Process Preserv, vol. 44, no. 1, Jan. 2020, doi: 10.1111/jfpp.14304. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpp.14304
M. K. I. Khan, M. Asif, Z. U. Razzaq, A. Nazir, and A. A. Maan, “Sustainable food industrial waste management through single cell protein production and characterization of protein enriched bread,” Food Bioscience, vol. 46, p. 101406, Apr. 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2021.101406. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbio.2021.101406
N. H. Aziz and G. I. Mohsen, “Bioconversion of acid- and gamma-ray-treated sweet potato residue to microbial protein by mixed cultures,” Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, vol. 29, no. 5, pp. 264–267, Nov. 2002, doi: 10.1038/sj.jim.7000297. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jim.7000297
S. M. Yap, J. C.-W. Lan, P. E. Kee, H. S. Ng, and H. S. Yim, “Enhancement of protein production using synthetic brewery wastewater by Haematococcus pluvialis,” Journal of Biotechnology, vol. 350, pp. 1–10, May 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2022.03.008. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2022.03.008
A. C. B. Ribeiro et al., “From mango by-product to food packaging: Pectin-phenolic antioxidant films from mango peels,” International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, vol. 193, pp. 1138–1150, Dec. 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.10.131. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.10.131
A. Mohsin et al., “Advances in sustainable approaches utilizing orange peel waste to produce highly value-added bioproducts,” Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, pp. 1–20, Dec. 2021, doi: 10.1080/07388551.2021.2002805. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/07388551.2021.2002805
B. L. Chua, S. F. Tang, A. Ali, and Y. H. Chow, “Optimisation of pectin production from dragon fruit peels waste: drying, extraction and characterisation studies,” SN Appl. Sci., vol. 2, no. 4, p. 621, Apr. 2020, doi: 10.1007/s42452-020-2415-y. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-020-2415-y
K. Asgari, M. Labbafi, F. Khodaiyan, M. Kazemi, and S. S. Hosseini, “High-methylated pectin from walnut processing wastes as a potential resource: Ultrasound assisted extraction and physicochemical, structural and functional analysis,” International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, vol. 152, pp. 1274–1282, Jun. 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.10.224. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.10.224
M. Grimaldi, O. Pitirollo, P. Ornaghi, C. Corradini, and A. Cavazza, “Valorization of agro-industrial byproducts: Extraction and analytical characterization of valuable compounds for potential edible active packaging formulation,” Food Packaging and Shelf Life, vol. 33, p. 100900, Sep. 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.fpsl.2022.100900. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fpsl.2022.100900
I. Benito-González, M. del M. Ortiz-Gimeno, A. López-Rubio, A. Martínez-Abad, A. Garrido-Fernández, and M. Martínez-Sanz, “Sustainable starch biocomposite films fully-based on white rice (Oryza sativa) agroindustrial by-products,” Food and Bioproducts Processing, vol. 136, pp. 47–58, Nov. 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.fbp.2022.09.008. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbp.2022.09.008
I. Costa-Trigo, P. Otero-Penedo, D. Outeiriño, A. Paz, and J. M. Domínguez, “Valorization of chestnut (Castanea sativa) residues: Characterization of different materials and optimization of the acid-hydrolysis of chestnut burrs for the elaboration of culture broths,” Waste Management, vol. 87, pp. 472–484, Mar. 2019, doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2019.02.028. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2019.02.028
A. T. Getachew, Y. J. Cho, and B. S. Chun, “Effect of pretreatments on isolation of bioactive polysaccharides from spent coffee grounds using subcritical water,” International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, vol. 109, pp. 711–719, Apr. 2018, doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.12.120. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.12.120
G. Marovska et al., “Lavender (Lavandula angustifolia Mill.) industrial by-products as a source of polysaccharides,” Industrial Crops and Products, vol. 188, p. 115678, Nov. 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2022.115678. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2022.115678
L. Bruno de Sousa Sabino et al., “Polysaccharides from acerola, cashew apple, pineapple, mango and passion fruit co-products: Structure, cytotoxicity and gastroprotective effects,” Bioactive Carbohydrates and Dietary Fibre, vol. 24, p. 100228, Oct. 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.bcdf.2020.100228. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcdf.2020.100228
J. J. Hora, E. R. Maydew, E. P. Lansky, and C. Dwivedi, “Chemopreventive Effects of Pomegranate Seed Oil on Skin Tumor Development in CD 1 Mice,” Journal of Medicinal Food, vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 157–161, Oct. 2003, doi: 10.1089/10966200360716553. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1089/10966200360716553
H.-L. Tian, P. Zhan, and K.-X. Li, “Analysis of components and study on antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of oil in apple seeds,” International Journal of Food Sciences and Nutrition, vol. 61, no. 4, pp. 395–403, Jun. 2010, doi: 10.3109/09637480903535772. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3109/09637480903535772
Y. Chen et al., “Antitumor activity of Annona squamosa seed oil,” Journal of Ethnopharmacology, vol. 193, pp. 362–367, Dec. 2016, doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.08.036. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2016.08.036
N. Bouazzaoui, J. Bouajila, S. Camy, J. K. Mulengi, and J.-S. Condoret, “Fatty acid composition, cytotoxicity and anti-inflammatory evaluation of melon ( Cucumis melo L. Inodorus ) seed oil extracted by supercritical carbon dioxide,” Separation Science and Technology, vol. 53, no. 16, pp. 2622–2627, Nov. 2018, doi: 10.1080/01496395.2018.1464579. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2018.1464579
F. Wang et al., “Antidiabetic Activity and Chemical Composition of Sanbai Melon Seed Oil,” Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, vol. 2018, pp. 1–14, 2018, doi: 10.1155/2018/5434156. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/5434156
M. I. Alkhalaf, W. S. Alansari, E. A. Ibrahim, and M. E. A. ELhalwagy, “Anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer activities of avocado (Persea americana) fruit and seed extract,” Journal of King Saud University - Science, vol. 31, no. 4, pp. 1358–1362, Oct. 2019, doi: 10.1016/j.jksus.2018.10.010. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2018.10.010
E. Rojo-Gutiérrez, J. J. Buenrostro-Figueroa, L. X. López-Martínez, D. R. Sepúlveda, and R. Baeza-Jiménez, “Biotechnological Potential of Cottonseed, a By-Product of Cotton Production,” in Valorisation of Agro-industrial Residues – Volume II: Non-Biological Approaches, Z. A. Zakaria, C. N. Aguilar, R. D. Kusumaningtyas, and P. Binod, Eds. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2020, pp. 63–82. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-39208-6_3. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-39208-6_3
L. Sepúlveda et al., “Ellagic acid production using polyphenols from orange peel waste by submerged fermentation,” Electronic Journal of Biotechnology, vol. 43, pp. 1–7, Jan. 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.ejbt.2019.11.002. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejbt.2019.11.002
M. Perra et al., “Combining Different Approaches for Grape Pomace Valorization: Polyphenols Extraction and Composting of the Exhausted Biomass,” Sustainability, vol. 14, no. 17, p. 10690, Aug. 2022, doi: 10.3390/su141710690. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/su141710690
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 EPISTEMUS

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
The magazine acquires the patrimonial rights of the articles only for diffusion without any purpose of profit, without diminishing the own rights of authorship.
The authors are the legitimate owners of the intellectual property rights of their respective articles, and in such quality, by sending their texts they express their desire to collaborate with the Epistemus Magazine, published biannually by the University of Sonora.
Therefore, freely, voluntarily and free of charge, once accepted the article for publication, they give their rights to the University of Sonora for the University of Sonora to edit, publish, distribute and make available through intranets, Internet or CD said work, without any limitation of form or time, as long as it is non-profit and with the express obligation to respect and mention the credit that corresponds to the authors in any use that is made of it.
It is understood that this authorization is not an assignment or transmission of any of your economic rights in favor of the said institution. The University of Sonora guarantees the right to reproduce the contribution by any means in which you are the author, subject to the credit being granted corresponding to the original publication of the contribution in Epistemus.
Unless otherwise indicated, all the contents of the electronic edition are distributed under a license for use and Creative Commons — Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International — (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0) You can consult here the informative version and the legal text of the license. This circumstance must be expressly stated in this way when necessary.
The names and email addresses entered in this journal will be used exclusively for the purposes established in it and will not be provided to third parties or for their use for other purposes.