Abordaje preventivo en la enfermedad por hígado graso no alcohólico
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.36790/epistemus.v16i32.185Palabras clave:
OBESIDAD, SALUD PUBLICA, COMPUESTOS BIOACTIVOS, HIGADO GRASO NO ALCOHOLICO, PREVENCION PRIMARIAResumen
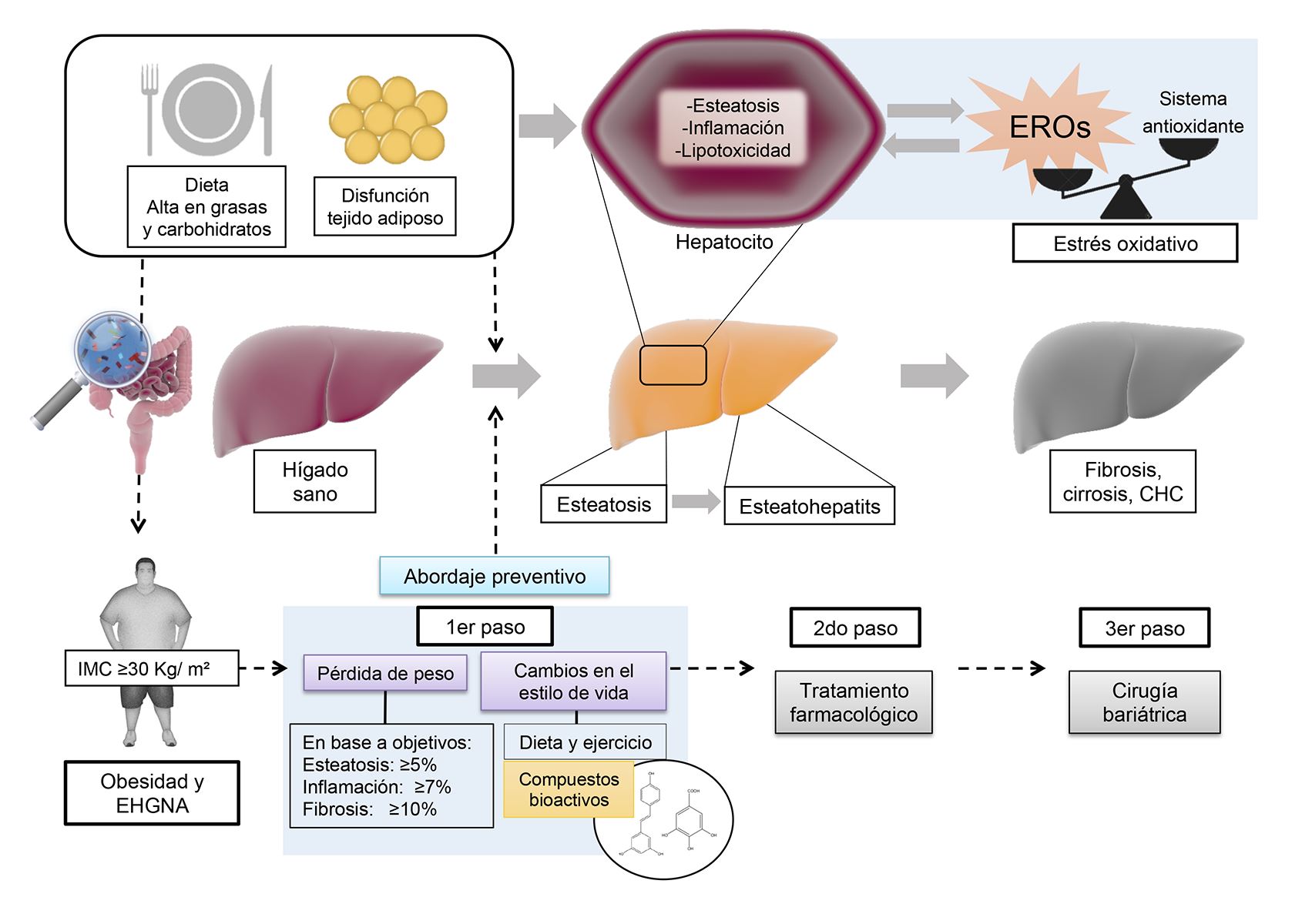
La obesidad es actualmente un problema de salud pública a nivel mundial. Ésta se caracteriza por afectar a múltiples órganos, entre ellos el hígado, desarrollándose enfermedades como la enfermedad de hígado graso no alcohólico (EHGNA), la cual predispone al desarrollo de carcinoma hepatocelular. En esta revisión se discute la asociación entre la obesidad y la EHGNA, enfatizando un abordaje preventivo y de intervención en etapas tempranas de la enfermedad, así como los potenciales efectos de algunos compuestos bioactivos presentes en la dieta. Al respecto es recomendable centrar la intervención en mejorar el IMC, a través de un programa de actividad física, educación nutricional y de salud, y cambios en los patrones dietéticos. La inclusión de alimentos ricos en compuestos bioactivos, como los compuestos fenólicos, fibra y vitaminas pueden proveer de un efecto antioxidante, antiinflamatorio y anti-obesogénico que podrían obstaculizar la progresión de la EHGNA, y otras comorbilidades y complicaciones.
Descargas
Citas
Y. C. Chooi, C. Ding, and F. Magkos, “The epidemiology of obesity,” Metabolism, vol. 92, pp. 6–10, Mar. 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2018.09.005
NCD Risk Factor Collaboration, “Trends in adult body-mass index in 200 countries from 1975 to 2014: a pooled analysis of 1698 population-based measurement studies with 19·2 million participants,” Lancet, vol. 387, no. 10026, pp. 1377–1396, Apr. 2016. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30054-X
R.-D. J. Shamah-Levy T, Romero-Martínez M, Barrientos-Gutiérrez T, Cuevas-Nasu L, Bautista-Arredondo S, Colchero MA, GaonaPineda EB, Lazcano-Ponce E, Martínez-Barnetche J, Alpuche-Arana C, “Encuesta Nacional de Salud y Nutrición 2020 sobre Covid-19. Resultados nacionales.,” Cuernavaca, México, 2021. [Online]. Available: https://ensanut.insp.mx/encuestas/ensanutcontinua2020/doctos/informes/ensanutCovid19ResultadosNacionales.pdf. DOI: https://doi.org/10.21149/12580
NCD Countdown 2030 collaborators, “NCD Countdown 2030: worldwide trends in non-communicable disease mortality and progress towards Sustainable Development Goal target 3.4.,” Lancet (London, England), vol. 392, no. 10152, pp. 1072–1088, 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31992-5
M. Aceves-Martins, E. Llauradó, L. Tarro, R. Solà, and M. Giralt, “Obesity-promoting factors in Mexican children and adolescents: challenges and opportunities.,” Glob. Health Action, vol. 9, p. 29625, 2016. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3402/gha.v9.29625
N. Chalasani et al., “The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.,” Hepatology, vol. 67, no. 1, pp. 328–357, 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.29367
Z. Younossi et al., “Global Perspectives on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis.,” Hepatology, vol. 69, no. 6, pp. 2672–2682, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.30251
M. M. Betancourt-Garcia, A. Arguelles, J. Montes, A. Hernandez, M. Singh, and R. A. Forse, “Pediatric Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: the Rise of a Lethal Disease Among Mexican American Hispanic Children,” Obes. Surg., vol. 27, no. 1, pp. 236–244, Jan. 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-016-2440-5
T. Arshad, J. M. Paik, R. Biswas, S. A. Alqahtani, L. Henry, and Z. M. Younossi, “Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Prevalence Trends Among Adolescents and Young Adults in the 2007‐2016,” Hepatol. Commun., vol. 5, no. 10, pp. 1676–1688, Oct. 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/hep4.1760
H. Hagström et al., “Adverse outcomes of pregnancy in women with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.,” Liver Int., vol. 36, no. 2, pp. 268–74, Feb. 2016. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/liv.12902
S. A. Alqahtani and J. M. Schattenberg, “NAFLD in the Elderly,” Clin. Interv. Aging, vol. 16, pp. 1633–1649, Sep. 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S295524
E. Buzzetti, M. Pinzani, and E. A. Tsochatzis, “The multiple-hit pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).,” Metabolism., vol. 65, no. 8, pp. 1038–48, Aug. 2016. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2015.12.012
D. E. Kleiner et al., “Association of Histologic Disease Activity With Progression of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease,” JAMA Netw. Open, vol. 2, no. 10, p. e1912565, Oct. 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.12565
A. Visekruna and M. Luu, “The Role of Short-Chain Fatty Acids and Bile Acids in Intestinal and Liver Function, Inflammation, and Carcinogenesis,” Front. Cell Dev. Biol., vol. 9, Jul. 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2021.703218
C. Rives et al., “Oxidative Stress in NAFLD: Role of Nutrients and Food Contaminants,” Biomolecules, vol. 10, no. 12, p. 1702, Dec. 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10121702
R. E. Patterson et al., “Lipotoxicity in steatohepatitis occurs despite an increase in tricarboxylic acid cycle activity,” Am. J. Physiol. Metab., vol. 310, no. 7, pp. E484–E494, Apr. 2016. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00492.2015
W. T. Garvey et al., “American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology Comprehensive Clinical Practice Guidelines Formedical Care of Patients with Obesity,” Endocr. Pract., vol. 22, pp. 1–203, Jul. 2016. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4158/EP161365.GL
A. Villani, J. Sultana, J. Doecke, and E. Mantzioris, “Differences in the interpretation of a modernized Mediterranean diet prescribed in intervention studies for the management of type 2 diabetes: how closely does this align with a traditional Mediterranean diet?,” Eur. J. Nutr., vol. 58, no. 4, pp. 1369–1380, Jun. 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-018-1757-3
Y. Ma, K. Chen, L. Lv, S. Wu, and Z. Guo, “Ferulic acid ameliorates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and modulates the gut microbiota composition in high-fat diet fed ApoE−/− mice,” Biomed. Pharmacother., vol. 113, p. 108753, May 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108753
R. Bernal-Reyes et al., “Consenso mexicano de la enfermedad por hígado graso no alcohólico,” Rev. Gastroenterol. México, vol. 84, no. 1, pp. 69–99, Jan. 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rgmx.2018.11.007
S. González, “Dietary Bioactive Compounds and Human Health and Disease,” Nutrients, vol. 12, no. 2, p. 348, Jan. 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12020348
Bo’ et al., “Systematic Review on Polyphenol Intake and Health Outcomes: Is there Sufficient Evidence to Define a Health-Promoting Polyphenol-Rich Dietary Pattern?,” Nutrients, vol. 11, no. 6, p. 1355, Jun. 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11061355
M. Świderska, M. Maciejczyk, A. Zalewska, J. Pogorzelska, R. Flisiak, and A. Chabowski, “Oxidative stress biomarkers in the serum and plasma of patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Can plasma AGE be a marker of NAFLD? Oxidative stress biomarkers in NAFLD patients.,” Free Radic. Res., vol. 53, no. 8, pp. 841–850, Aug. 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/10715762.2019.1635691
M. Fukaya, Y. Sato, S. Kondo, S. Adachi, F. Yoshizawa, and Y. Sato, “Quercetin enhances fatty acid β-oxidation by inducing lipophagy in AML12 hepatocytes,” Heliyon, vol. 7, no. 6, p. e07324, Jun. 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e07324
N. M. El-Lakkany et al., “Antifibrotic effects of gallic acid on hepatic stellate cells: In vitro and in vivo mechanistic study,” J. Tradit. Complement. Med., vol. 9, no. 1, pp. 45–53, Jan. 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcme.2018.01.010
P. Dey, B. D. Olmstead, G. Y. Sasaki, Y. Vodovotz, Z. Yu, and R. S. Bruno, “Epigallocatechin gallate but not catechin prevents nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in mice similar to green tea extract while differentially affecting the gut microbiota,” J. Nutr. Biochem., vol. 84, p. 108455, Oct. 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2020.108455
J. Li et al., “Green tea extract protects against hepatic NFκB activation along the gut-liver axis in diet-induced obese mice with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis by reducing endotoxin and TLR4/MyD88 signaling,” J. Nutr. Biochem., vol. 53, pp. 58–65, Mar. 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2017.10.016
H.-N. Mu et al., “Caffeic acid prevents non-alcoholic fatty liver disease induced by a high-fat diet through gut microbiota modulation in mice,” Food Res. Int., vol. 143, p. 110240, May 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110240
D. Ivancovsky-Wajcman et al., “Dietary vitamin E and C intake is inversely associated with the severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease,” Dig. Liver Dis., vol. 51, no. 12, pp. 1698–1705, Dec. 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dld.2019.06.005
Y. Fukuzawa, M. P. Kapoor, K. Yamasaki, T. Okubo, Y. Hotta, and L. R. Juneja, “Effects of green tea catechins on nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) patients,” J. Funct. Foods, vol. 9, pp. 48–59, Jul. 2014. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2014.04.010
U. Hayat, A. A. Siddiqui, H. Okut, S. Afroz, S. Tasleem, and A. Haris, “The effect of coffee consumption on the non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and liver fibrosis: A meta-analysis of 11 epidemiological studies,” Ann. Hepatol., vol. 20, p. 100254, Jan. 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aohep.2020.08.071
S. Rafiee, H. Mohammadi, A. Ghavami, E. Sadeghi, Z. Safari, and G. Askari, “Efficacy of resveratrol supplementation in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials,” Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract., vol. 42, p. 101281, Feb. 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctcp.2020.101281
M. Mazidi, N. Katsiki, and M. Banach, “A higher flavonoid intake is associated with less likelihood of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: results from a multiethnic study,” J. Nutr. Biochem., vol. 65, pp. 66–71, Mar. 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2018.10.001
Publicado
Cómo citar
Número
Sección
Licencia
Derechos de autor 2022 EPISTEMUS

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-CompartirIgual 4.0.
La revista adquiere los derechos patrimoniales de los artículos sólo para difusión sin ningún fin de lucro, sin menoscabo de los propios derechos de autoría.
Los autores son los legítimos titulares de los derechos de propiedad intelectual de sus respectivos artículos, y en tal calidad, al enviar sus textos expresan su deseo de colaborar con la Revista Epistemus, editada semestralmente por la Universidad de Sonora.
Por lo anterior, de manera libre, voluntaria y a título gratuito, una vez aceptado el artículo para su publicación, ceden sus derechos a la Universidad de Sonora para que la Universidad de Sonora edite, publique, distribuya y ponga a disposición a través de intranets, internet o CD dicha obra, sin limitación alguna de forma o tiempo, siempre y cuando sea sin fines de lucro y con la obligación expresa de respetar y mencionar el crédito que corresponde a los autores en cualquier utilización que se haga del mismo.
Queda entendido que esta autorización no es una cesión o transmisión de alguno de sus derechos patrimoniales en favor de la mencionada institución. La UniSon le garantiza el derecho de reproducir la contribución por cualquier medio en el cual usted sea el autor, sujeto a que se otorgue el crédito correspondiente a la publicación original de la contribución en Epistemus.
Salvo indicación contraria, todos los contenidos de la edición electrónica se distribuyen bajo una licencia de uso y Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0) Puede consultar desde aquí la versión informativa y el texto legal de la licencia. Esta circunstancia ha de hacerse constar expresamente de esta forma cuando sea necesario.