Three-Way Catalysts: History, Performance and Environmental Advantages
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.36790/epistemus.v16i33.240Keywords:
Catalysts, atmospheric pollution, gas emissions, Vehicular trafficAbstract
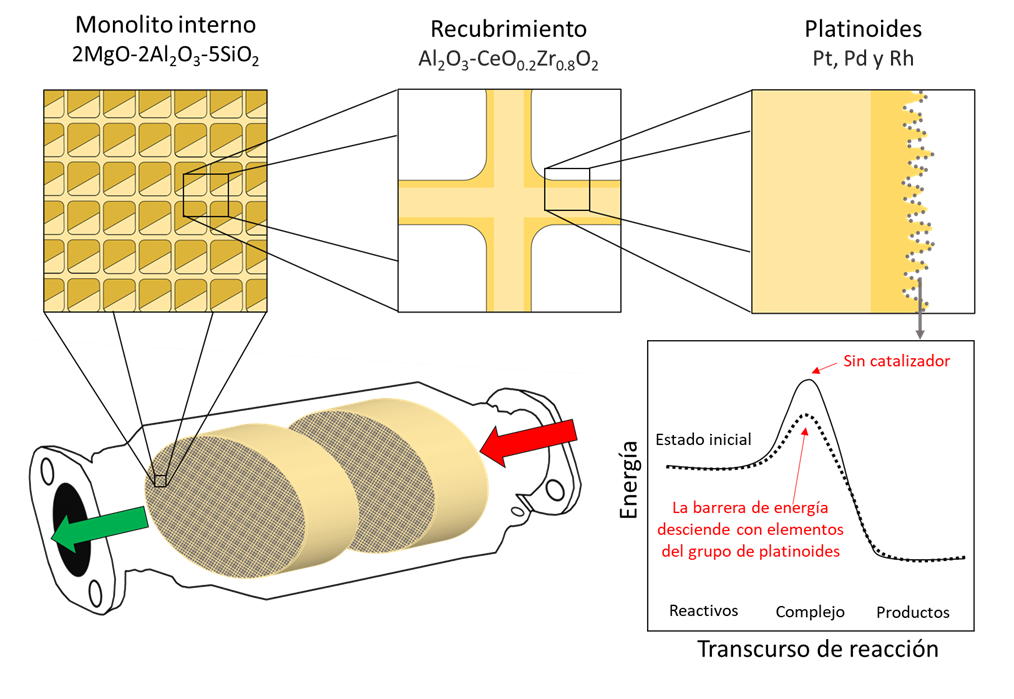
Three-way catalyst is a tool used to reduce the emission of pollutant gases released by an automobile's internal combustion engine. This paper aims to provide an understanding of the operation and the importance of the three-way catalyst. A general description of the historical evolution of their development, up to the formulation and structure of current catalysts, is presented. In addition, their operation at the molecular level and the operating conditions that ensure their conversion efficiency are described. We discuss the advantages to the environment and human health that come along with their proper use. Finally, the importance of their timely replacement is highlighted.
Downloads
References
TransportPolicy.net. "Topics: Emissions standards." (Revisado el 14 de agosto del 2022).
A. M. D. L. I. AUTOMOTRIZ, A. G. D. D. FEDERAL, G. D. E. DE MEXICO, and P. F. D. P. AL AMBIENTE, "NOM-042-SEMARNAT-2003: Que Establece los Límites Máximos Permisibles de Emisión de Hidrocarburos Totales o no Metano, Monóxido de Carbono, Óxidos de Nitrógeno y Partículas Provenientes del Escape de los Vehículos Automotores Nuevos Cuyo Peso Bruto Vehicular no Exceda los 3,857."
S. Dey and N. S. Mehta, "Automobile pollution control using catalysis," Res Environ Sustain, vol. 2, p. 100006, 2020/12/01/ 2020, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resenv.2020.100006. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resenv.2020.100006
R. J. Farrauto, M. Deeba, and S. Alerasool, "Gasoline automobile catalysis and its historical journey to cleaner air," Nature Catalysis, vol. 2, no. 7, pp. 603-613, 2019, doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41929-019-0312-9. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41929-019-0312-9
L. Hegedus and J. C. Summers, "Platinum-rhodium catalyst for automotive emission control," ed: Google Patents, 1978.
S. Dey and G. C. Dhal, "Cerium catalysts applications in carbon monoxide oxidations," Mat Sci Energy Technol, vol. 3, pp. 6-24, 2020, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mset.2019.09.003. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mset.2019.09.003
B. M. Reddy, A. Khan, P. Lakshmanan, M. Aouine, S. Loridant, and J.-C. Volta, "Structural characterization of nanosized CeO2− SiO2, CeO2− TiO2, and CeO2− ZrO2 catalysts by XRD, Raman, and HREM techniques," J Phys Chem B
vol. 109, no. 8, pp. 3355-3363, 2005, doi: https://doi.org/10.1021/jp045193h. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jp045193h
T. Montini, M. Melchionna, M. Monai, and P. Fornasiero, "Fundamentals and catalytic applications of CeO2-based materials," Chem Rev, vol. 116, no. 10, pp. 5987-6041, 2016, doi: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00603. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00603
M. Yao, R. Baird, F. Kunz, and T. Hoost, "An XRD and TEM investigation of the structure of alumina-supported ceria–zirconia," J Catal vol. 166, no. 1, pp. 67-74, 1997, doi: https://doi.org/10.1006/jcat.1997.1504. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/jcat.1997.1504
V. Gupta, K. Chaturvedi, M. Dubey, and N. M. Rao, "Catalytic converters for treatment of exhaust gas emission in automobiles: a review," Int J Scient Eng Res, vol. 8, no. 2, pp. 95-99, 2017.
R. Zanella, "Aplicación de los nanomateriales en catálisis," Mundo nano. Revista interdisciplinaria en nanociencias y nanotecnología, vol. 7, no. 12, pp. 66-82, 2014. DOI: https://doi.org/10.22201/ceiich.24485691e.2014.12.49711
E. Kritsanaviparkporn, F. M. Baena-Moreno, and T. R. Reina, "Catalytic converters for vehicle exhaust: fundamental aspects and technology overview for newcomers to the field," Chemistry, vol. 3, no. 2, pp. 630-646, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry3020044. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry3020044
C. Mattiuzzi and G. Lippi, "Worldwide epidemiology of carbon monoxide poisoning," Hum Exp Toxicol, vol. 39, no. 4, pp. 387-392, 2020, doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/0960327119891214. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/0960327119891214
K. Sun, Y. Song, F. He, M. Jing, J. Tang, and R. Liu, "A review of human and animals exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Health risk and adverse effects, photo-induced toxicity and regulating effect of microplastics," Sci Total Environ, vol. 773, p. 145403, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145403. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145403
B. P. Barrick, U. Jain, and M. M. Herr, "Environmental and health impacts of nitrous oxide in current medical practice," ASA Monitor, vol. 84, no. 4, pp. 22-25, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/01.M99.0000695152.94898.49
D. Meza-Figueroa, M. Pedroza-Montero, M. Barboza-Flores, S. Navarro-Espinoza, R. Ruiz-Torres, A. Robles-Morúa, F. Romero, B. Schiavo, B. González-Grijalva, and M. Acosta-Elias, "Identification of refractory zirconia from catalytic converters in dust: An emerging pollutant in urban environments," Sci Total Environ, vol. 760, p. 143384, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143384. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143384
M. Omrani, M. Goriaux, Y. Liu, S. Martinet, L. Jean-Soro, and V. Ruban, "Platinum group elements study in automobile catalysts and exhaust gas samples," Environ Poll, vol. 257, p. 113477, 2020, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113477. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113477
S. Y. Christou, S. García-Rodríguez, J. L. G. Fierro, and A. M. Efstathiou, "Deactivation of Pd/Ce0.5Zr0.5O2 model three-way catalyst by P, Ca and Zn deposition," Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, vol. 111, pp. 233-245, 2012. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2011.10.004
S. Navarro-Espinoza, D. Meza-Figueroa, R. Guzmán, A. Duarte-Moller, H. Esparza-Ponce, F. Paz-Moreno, B. González-Grijalva, O. Álvarez-Bajo, B. Schiavo, D. Soto-Puebla, and M. Pedroza-Montero, "Release of Nanoparticles in the Environment and Catalytic Converters Ageing," Nanomaterials, vol. 11, no. 12, p. 3406, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11123406. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11123406
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 EPISTEMUS

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
The magazine acquires the patrimonial rights of the articles only for diffusion without any purpose of profit, without diminishing the own rights of authorship.
The authors are the legitimate owners of the intellectual property rights of their respective articles, and in such quality, by sending their texts they express their desire to collaborate with the Epistemus Magazine, published biannually by the University of Sonora.
Therefore, freely, voluntarily and free of charge, once accepted the article for publication, they give their rights to the University of Sonora for the University of Sonora to edit, publish, distribute and make available through intranets, Internet or CD said work, without any limitation of form or time, as long as it is non-profit and with the express obligation to respect and mention the credit that corresponds to the authors in any use that is made of it.
It is understood that this authorization is not an assignment or transmission of any of your economic rights in favor of the said institution. The University of Sonora guarantees the right to reproduce the contribution by any means in which you are the author, subject to the credit being granted corresponding to the original publication of the contribution in Epistemus.
Unless otherwise indicated, all the contents of the electronic edition are distributed under a license for use and Creative Commons — Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International — (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0) You can consult here the informative version and the legal text of the license. This circumstance must be expressly stated in this way when necessary.
The names and email addresses entered in this journal will be used exclusively for the purposes established in it and will not be provided to third parties or for their use for other purposes.